A set of novel attack procedures has been shown against Google Workspace and the Google Cloud Platform that could be potentially leveraged by threat actors to perform ransomware, details exfiltration, and password recovery attacks.
“Setting up from a one compromised machine, threat actors could progress in several strategies: they could move to other cloned machines with GCPW set up, gain accessibility to the cloud system with custom permissions, or decrypt locally stored passwords to continue on their attack further than the Google ecosystem,” Martin Zugec, specialized options director at Bitdefender, mentioned in a new report.
A prerequisite for these assaults is that the undesirable actor has by now obtained access to a neighborhood equipment by means of other means, prompting Google to mark the bug as not suitable for repairing “since it can be outside of our risk model and the conduct is in line with Chrome’s methods of storing neighborhood knowledge.”

Nonetheless, the Romanian cybersecurity business has warned that danger actors can exploit this kind of gaps to lengthen a one endpoint compromise to a network-extensive breach.
The attacks, in a nutshell, rely on an organization’s use of Google Credential Provider for Windows (GCPW), which offers equally cellular product management (MDM) and single indicator-on (SSO) abilities.
This allows directors to remotely control and control Windows products in their Google Workspace environments, as properly as permits people to obtain their Windows equipment working with the exact qualifications that are used to login to their Google accounts.
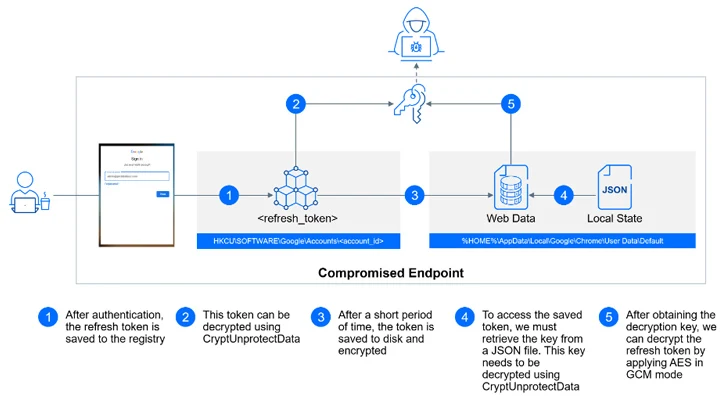
GCPW is developed to use a community privileged support account named Google Accounts and ID Administration (GAIA) to seamlessly aid the approach in the qualifications by connecting to Google APIs for verifying a user’s credentials for the duration of the indication-in phase and storing a refresh token to obviate the have to have for re-authentication.
With this setup in spot, an attacker with accessibility to a compromised equipment can extract an account’s refresh OAuth tokens, either from the Windows registry or from the user’s Chrome profile directory, and bypass multi-component authentication (MFA) protections.
The refresh token is subsequently used to build an HTTP Article request to the endpoint “https://www.googleapis[.]com/oauth2/v4/token” to attain an access token, which, in turn, can be abused to retrieve, manipulate, or delete sensitive information linked with the Google Account.

A 2nd exploit problems what’s termed the Golden Picture lateral motion, which focuses on virtual device (VM) deployments and will take edge of the simple fact that generating a machine by cloning yet another device with pre-set up GCPW brings about the password related with the GAIA account to be cloned as well.
“If you know the password to a neighborhood account, and nearby accounts on all machines share the same password, then you know the passwords to all devices,” Zugec stated.
“This shared-password challenge is very similar to getting the identical community administrator password on all machines that has been tackled by Microsoft’s Community Administrator Password Remedy (LAPS).”
The 3rd attack entails accessibility to plaintext qualifications by leveraging the access token obtained utilizing the aforementioned strategy to send out an HTTP GET request to an undocumented API endpoint and get hold of the personal RSA key that is required to decrypt the password industry.
“Obtaining accessibility to plaintext qualifications, such as usernames and passwords, signifies a extra significant risk,” Zugec mentioned. “This is due to the fact it enables attackers to straight impersonate legitimate users and obtain unrestricted obtain to their accounts, perhaps leading to finish account takeover.”
Identified this report appealing? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to browse a lot more special written content we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Russian Hackers Launch ‘Largest Ever Cyber Attack’ on Danish Critical Infrastructure
Russian Hackers Launch ‘Largest Ever Cyber Attack’ on Danish Critical Infrastructure