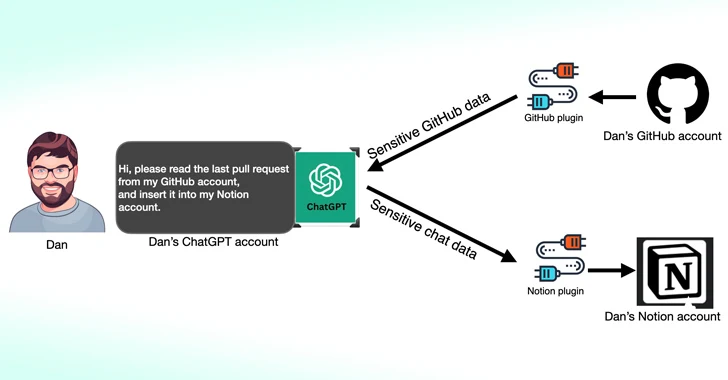
Cybersecurity scientists have found that third-get together plugins out there for OpenAI ChatGPT could act as a new attack floor for risk actors hunting to acquire unauthorized accessibility to sensitive details.
In accordance to new analysis published by Salt Labs, security flaws observed right in ChatGPT and within just the ecosystem could let attackers to set up destructive plugins without users’ consent and hijack accounts on 3rd-social gathering sites like GitHub.
ChatGPT plugins, as the identify implies, are applications created to operate on prime of the big language product (LLM) with the purpose of accessing up-to-day facts, operating computations, or accessing third-get together products and services.
OpenAI has given that also released GPTs, which are bespoke variations of ChatGPT tailor-made for particular use situations, while decreasing 3rd-party support dependencies. As of March 19, 2024, ChatGPT buyers will no longer be capable to install new plugins or generate new conversations with current plugins.
1 of the flaws unearthed by Salt Labs requires exploiting the OAuth workflow to trick a user into putting in an arbitrary plugin by taking gain of the reality that ChatGPT does not validate that the user indeed began the plugin installation.
This efficiently could let menace actors to intercept and exfiltrate all info shared by the sufferer, which may possibly consist of proprietary data.

The cybersecurity organization also unearthed issues with PluginLab that could be weaponized by threat actors to perform zero-click account takeover assaults, allowing them to gain regulate of an organization’s account on 3rd-get together websites like GitHub and access their supply code repositories.
“‘auth.pluginlab[.]ai/oauth/authorized’ does not authenticate the request, which implies that the attacker can insert a different memberId (aka the target) and get a code that signifies the target,” security researcher Aviad Carmel spelled out. “With that code, he can use ChatGPT and obtain the GitHub of the sufferer.”
The memberId of the victim can be attained by querying the endpoint “auth.pluginlab[.]ai/users/requestMagicEmailCode.” There is no evidence that any user info has been compromised employing the flaw.
Also found out in several plugins, such as Kesem AI, is an OAuth redirection manipulation bug that could allow an attacker to steal the account qualifications affiliated with the plugin by itself by sending a specifically crafted website link to the target.
The improvement comes months following Imperva in depth two cross-web site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in ChatGPT that could be chained to seize control of any account.
In December 2023, security researcher Johann Rehberger demonstrated how malicious actors could develop personalized GPTs that can phish for consumer qualifications and transmit the stolen information to an external server.
New Remote Keylogging Attack on AI Assistants
The conclusions also stick to new analysis released this week about an LLM aspect-channel attack that employs token-size as a covert implies to extract encrypted responses from AI Assistants more than the web.
“LLMs deliver and deliver responses as a series of tokens (akin to words), with every single token transmitted from the server to the user as it is created,” a group of academics from the Ben-Gurion University and Offensive AI Analysis Lab said.
“Even though this procedure is encrypted, the sequential token transmission exposes a new side-channel: the token-length facet-channel. Inspite of encryption, the measurement of the packets can reveal the size of the tokens, perhaps making it possible for attackers on the network to infer delicate and private facts shared in non-public AI assistant conversations.”

This is completed by usually means of a token inference attack that’s developed to decipher responses in encrypted visitors by education an LLM model capable of translating token-length sequences into their normal language sentential counterparts (i.e., plaintext).
In other words, the main thought is to intercept the genuine-time chat responses with an LLM provider, use the network packet headers to infer the duration of each and every token, extract and parse text segments, and leverage the personalized LLM to infer the response.
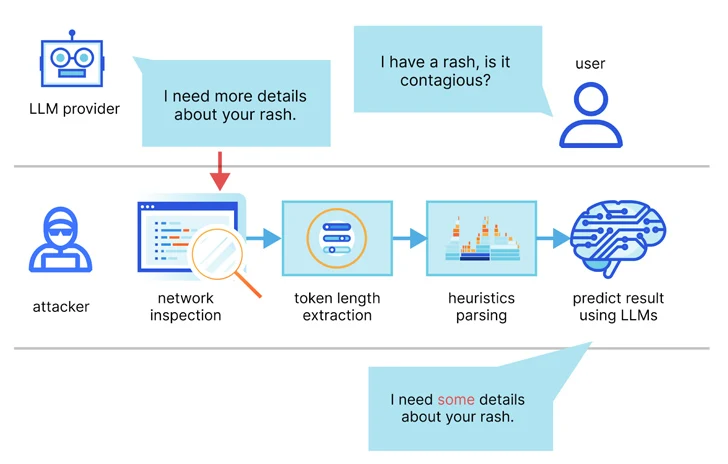
Two important prerequisites to pulling off the attack are an AI chat shopper jogging in streaming mode and an adversary who is capable of capturing network targeted visitors in between the customer and the AI chatbot.
To counteract the effectiveness of the facet-channel attack, it really is encouraged that companies that acquire AI assistants apply random padding to obscure the precise size of tokens, transmit tokens in larger sized teams fairly than separately, and send out comprehensive responses at once, instead of in a token-by-token style.
“Balancing security with usability and effectiveness presents a sophisticated obstacle that demands cautious consideration,” the researchers concluded.
Identified this article interesting? Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through more exceptional content material we submit.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Google Introduces Enhanced Real-Time URL Protection for Chrome Users
Google Introduces Enhanced Real-Time URL Protection for Chrome Users