U.S. cybersecurity and intelligence organizations have warned of Phobos ransomware assaults concentrating on federal government and critical infrastructure entities, outlining the several practices and techniques the danger actors have adopted to deploy the file-encrypting malware.
“Structured as a ransomware as a assistance (RaaS) product, Phobos ransomware actors have specific entities together with municipal and county governments, emergency products and services, training, community healthcare, and critical infrastructure to productively ransom a number of million in U.S. pounds,” the federal government mentioned.
The advisory arrives from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Company (CISA), the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), and the Multi-Condition Info Sharing and Examination Middle (MS-ISAC).
Lively considering the fact that May possibly 2019, various variants of Phobos ransomware have been determined to day, particularly Eking, 8, Elbie, Devos, Faust, and Backmydata. Late last 12 months, Cisco Talos exposed that the menace actors powering the 8Base ransomware are leveraging a Phobos ransomware variant to conduct their financially enthusiastic attacks.
There is proof to recommend that Phobos is most likely closely managed by a central authority, which controls the ransomware’s private decryption important.
Attack chains involving the ransomware strain have generally leveraged phishing as an first access vector to drop stealthy payloads like SmokeLoader. Alternatively, susceptible networks are breached by searching for uncovered RDP expert services and exploiting them by implies of a brute-force attack.

A successful electronic crack-in is adopted by the risk actors dropping further remote accessibility resources, taking gain of process injection methods to execute destructive code and evade detection, and earning Windows Registry modifications to manage persistence in just compromised environments.
“On top of that, Phobos actors have been observed working with developed-in Windows API features to steal tokens, bypass entry controls, and make new processes to escalate privileges by leveraging the SeDebugPrivilege course of action,” the businesses explained. “Phobos actors endeavor to authenticate making use of cached password hashes on target machines right up until they access area administrator obtain.”
The e-criminal offense team is also regarded to use open-resource instruments these kinds of as Bloodhound and Sharphound to enumerate the active listing. File exfiltration is achieved by using WinSCP and Mega.io, following which volume shadow copies are deleted in an endeavor to make recovery harder.
The disclosure comes as Bitdefender thorough a meticulously coordinated ransomware attack impacting two separate companies at the identical time. The attack, described as synchronized and multifaceted, has been attributed to a ransomware actor referred to as CACTUS.
“CACTUS continued infiltrating the network of a single corporation, implanting a variety of kinds of remote entry instruments and tunnels across various servers,” Martin Zugec, specialized solutions director at Bitdefender, explained in a report revealed final week.
“When they discovered an option to shift to one more company, they momentarily paused their procedure to infiltrate the other network. Both corporations are aspect of the same team, but run independently, retaining individual networks and domains without the need of any proven belief marriage.”
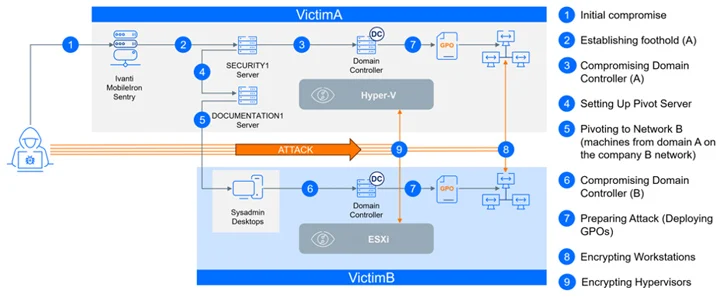
The attack is also notable for the concentrating on of the unnamed firm’s virtualization infrastructure, indicating that CACTUS actors have broadened their aim further than Windows hosts to strike Hyper-V and VMware ESXi hosts.
It also leveraged a critical security flaw (CVE-2023-38035, CVSS score: 9.8) in an internet-exposed Ivanti Sentry server considerably less than 24 several hours soon after its preliminary disclosure in August 2023, at the time all over again highlighting opportunistic and rapid weaponization of recently printed vulnerabilities.

Ransomware continues to be a major dollars spinner for financially determined threat actors, with initial ransomware calls for achieving a median of $600,000 in 2023, a 20% jump from the former year, in accordance to Arctic Wolf. As of Q4 2023, the normal ransom payment stands at $568,705 per sufferer.
What is actually extra, having to pay a ransom demand from customers does not amount of money to foreseeable future safety. There is no assurance that a victim’s details and programs will be securely recovered and that the attackers will never sell the stolen knowledge on underground message boards or attack them again.
Information shared by cybersecurity business Cybereason demonstrates that “a staggering 78% [of organizations] had been attacked all over again right after shelling out the ransom – 82% of them inside of a calendar year,” in some scenarios by the identical danger actor. Of these victims, 63% ended up “requested to pay far more the next time.”
Identified this report attention-grabbing? Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to examine far more distinctive information we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 U.S. Court Orders NSO Group to Hand Over Pegasus Spyware Code to WhatsApp
U.S. Court Orders NSO Group to Hand Over Pegasus Spyware Code to WhatsApp