The U.S. Countrywide Security Agency (NSA) on Thursday unveiled assistance to assistance corporations detect and protect against bacterial infections of a Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) bootkit identified as BlackLotus.
To that finish, the agency is recommending that “infrastructure homeowners get action by hardening person executable policies and checking the integrity of the boot partition.”
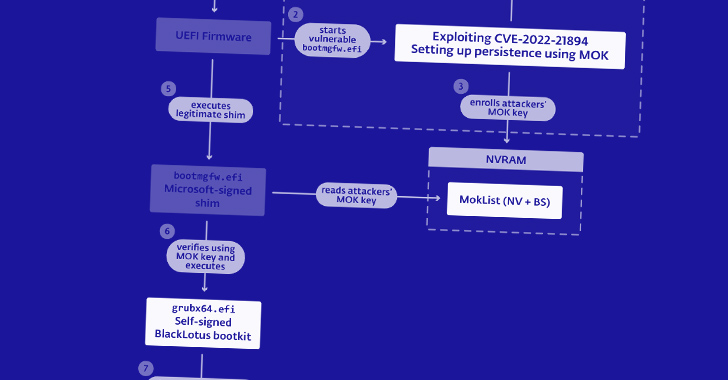
BlackLotus is an superior crimeware answer that was first spotlighted in October 2022 by Kaspersky. A UEFI bootkit able of bypassing Windows Safe Boot protections, samples of the malware have considering the fact that emerged in the wild.

This is completed by using advantage of a known Windows flaw known as Baton Drop (CVE-2022-21894, CVSS score: 4.4) identified in vulnerable boot loaders not extra into the Safe Boot DBX revocation listing. The vulnerability was resolved by Microsoft in January 2022.
This loophole could be exploited by danger actors to substitute entirely patched boot loaders with vulnerable variations and execute BlackLotus on compromised endpoints.
UEFI bootkits like BlackLotus grant a menace actor full management above the working program booting method, therefore making it doable to interfere with security mechanisms and deploy more payloads with elevated privileges.
It can be well worth noting that BlackLotus is not a firmware threat, and alternatively hones in on the earliest software program phase of the boot approach to reach persistence and evasion. There is no proof that the malware targets Linux techniques.
“UEFI bootkits may possibly eliminate on stealthiness when in comparison to firmware implants […] as bootkits are situated on an easily available Fat32 disk partition,” ESET researcher Martin Smolár mentioned in an assessment of BlackLotus in March 2023.
“However, functioning as a bootloader provides them virtually the similar abilities as firmware implants, but without having to triumph over the multilevel SPI flash defenses, this sort of as the BWE, BLE, and PRx safety bits, or the protections delivered by components (like Intel Boot Guard).
Aside from applying the Could 2023 Patch Tuesday updates from Microsoft, which dealt with a next Safe Boot bypass flaw (CVE-2023-24932, CVSS score: 6.7) exploited by BlackLotus, businesses are advised to have out the subsequent mitigation measures –
- Update recovery media
- Configure defensive program to scrutinize variations to the EFI boot partition
- Watch device integrity measurements and boot configuration for anomalous variations in the EFI boot partition
- Customise UEFI Secure Boot to block more mature, signed Windows boot loaders
- Clear away the Microsoft Windows Output CA 2011 certification on devices that exclusively boot Linux
Microsoft, for its part, is using a phased tactic to totally shut the attack vector. The fixes are expected to be commonly out there in the 1st quarter of 2024.
Discovered this short article appealing? Stick to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through a lot more exceptional written content we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 New Cryptocurrency Mining Campaign Targets Linux Systems and IoT Devices
New Cryptocurrency Mining Campaign Targets Linux Systems and IoT Devices