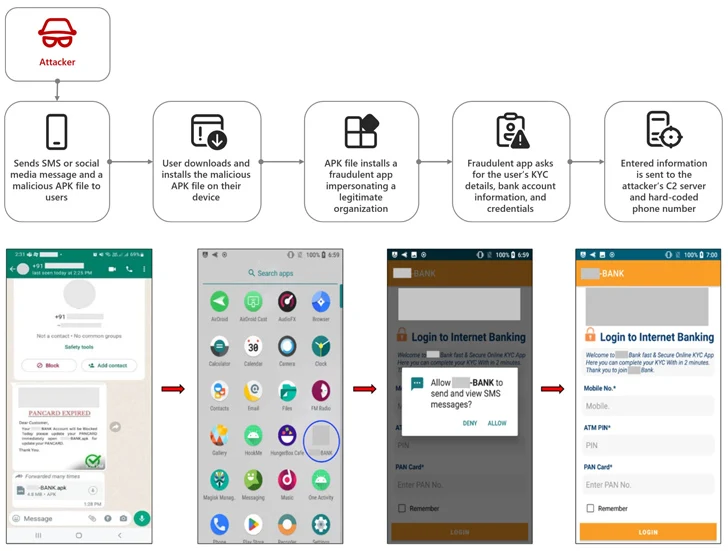
Android smartphone consumers in India are the focus on of a new malware marketing campaign that employs social engineering lures to install fraudulent apps that are capable of harvesting sensitive details.
“Working with social media platforms like WhatsApp and Telegram, attackers are sending messages designed to lure users into setting up a destructive app on their cellular machine by impersonating genuine corporations, this kind of as banks, federal government companies, and utilities,” Microsoft threat intelligence scientists Abhishek Pustakala, Harshita Tripathi, and Shivang Desai mentioned in a Monday assessment.
The supreme intention of the procedure is to seize banking aspects, payment card facts, account qualifications, and other individual facts.
The attack chains require sharing malicious APK data files via social media messages sent on WhatsApp and Telegram by falsely presenting them as banking apps and inducing a feeling of urgency by claiming that the targets’ bank accounts will be blocked unless they update their long lasting account number (PAN) issued by the Indian Earnings Tax Section by the bogus app.
On set up, the app urges the sufferer to enter their financial institution account details, debit card PIN, PAN card figures, and online banking credentials, which are subsequently transmitted to an actor-managed command-and-management (C2) server and a hard-coded phone selection.

“At the time all the requested facts are submitted, a suspicious note appears stating that the particulars are currently being verified to update KYC,” the scientists reported.
“The consumer is instructed to wait around 30 minutes and not to delete or uninstall the application. On top of that, the application has the performance to cover its icon, creating it to vanish from the user’s unit dwelling display screen while even now working in the track record.”
A different noteworthy factor of the malware is that it requests the user to grant it authorization to study and ship SMS messages, therefore enabling it to intercept 1-time passwords (OTPs) and ship the victims’ messages to the danger actor’s phone selection through SMS.
Variants of the banking trojan uncovered by Microsoft have also been located to steal credit history card specifics alongside with personally identifiable details (PII) and incoming SMS messages, exposing unsuspecting consumers to economic fraud.
Nonetheless, it really is worthy of noting that for these attacks to be prosperous, buyers will have to empower the possibility to install apps from not known sources exterior of the Google Perform Retailer.
“Cellular banking trojan infections can pose important risks to users’ personalized details, privateness, unit integrity, and economic security,” the scientists reported. “These threats can frequently disguise on their own as reputable applications and deploy social engineering ways to realize their ambitions and steal users’ sensitive details and economic property.”
The progress will come as the Android ecosystem has also occur beneath attack from the SpyNote trojan, which has targeted Roblox users below the guise of a mod to siphon sensitive data.
In one more instance, pretend grownup web-sites are remaining used as lures to entice consumers into downloading an Android malware known as Enchant that specially focuses on pilfering data from cryptocurrency wallets.
“Enchant malware employs the accessibility assistance attribute to goal specific cryptocurrency wallets, together with imToken, OKX, Bitpie Wallet, and TokenPocket wallet,” Cyble said in a recent report.
“Its major goal is to steal critical info this kind of as wallet addresses, mnemonic phrases, wallet asset particulars, wallet passwords, and private keys from compromised equipment.”

Last month, Medical professional Web uncovered numerous destructive apps on the Google Participate in Store that exhibited intrusive advertisements (HiddenAds), subscribed end users to top quality products and services with no their knowledge or consent (Joker), and promoted investment decision scams by masquerading as buying and selling software package (FakeApp).
The onslaught of Android malware has prompted Google to announce new security characteristics this kind of as genuine-time code-stage scanning for freshly encountered apps. It also launched limited configurations with Android 13 that prohibits applications from acquiring obtain to critical unit configurations (e.g., accessibility) until it truly is explicitly enabled by the person.
It’s not just Google. Samsung, in late Oct 2023, unveiled a new Car Blocker choice that stops application installations from sources other than Google Participate in Retailer and Galaxy Shop, and blocks destructive commands and software package installations by the USB port.
To keep away from downloading malicious computer software from Google Engage in and other trustworthy resources, consumers are suggested to examine the legitimacy of the application builders, scrutinize evaluations, and vet the permissions asked for by the applications.
Discovered this post interesting? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through more distinctive content material we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Mustang Panda Hackers Targets Philippines Government Amid South China Sea Tensions
Mustang Panda Hackers Targets Philippines Government Amid South China Sea Tensions