XWorm is a fairly new agent of the distant access trojan cohort that has already gained its location between the most persistent threats throughout the globe.
Due to the fact 2022, when it was 1st observed by researchers, it has undergone a number of big updates that have significantly increased its operation and solidified its being electricity.
The analyst workforce at ANY.Run came across the latest version of the malware and could not refuse the prospect of using it aside to look at XWorm mechanics configurations. In this article is how they did it and what they located.
The XWorm sample’s source
The sample in concern was discovered in ANY. RUN’s databases of malware, a repository made up of comprehensive evaluation experiences on all data files and links that have been uploaded by buyers of the sandbox in community manner.
A brief glance at the outcomes of the investigation revealed that the sample was to begin with dispersed via MediaFire, a file-hosting services. The malware was packaged in a RAR archive and protected by a password.
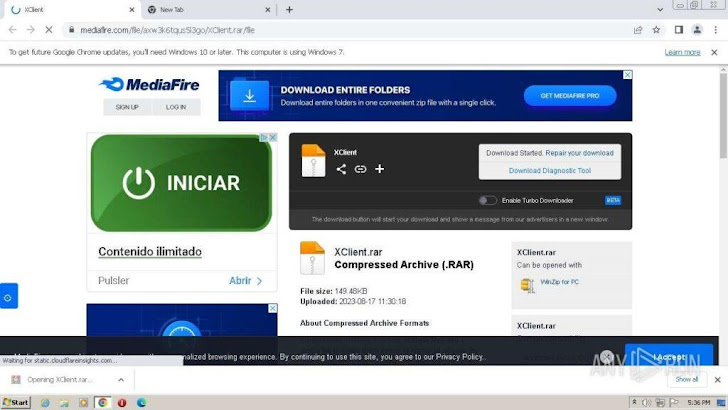 Determine 1: The MediaFire webpage made up of the archive obtain website link.
Determine 1: The MediaFire webpage made up of the archive obtain website link.
On execution, the threat was instantly detected by Suricata regulations and recognized as XWorm.
 Determine 2: XWorm’s targeted traffic marked as malicious by the sandbox.
Determine 2: XWorm’s targeted traffic marked as malicious by the sandbox.
XWorm’s Techniques, Techniques, and Processes (TTPs)
The sandbox report highlighted numerous procedures utilized by the sample:
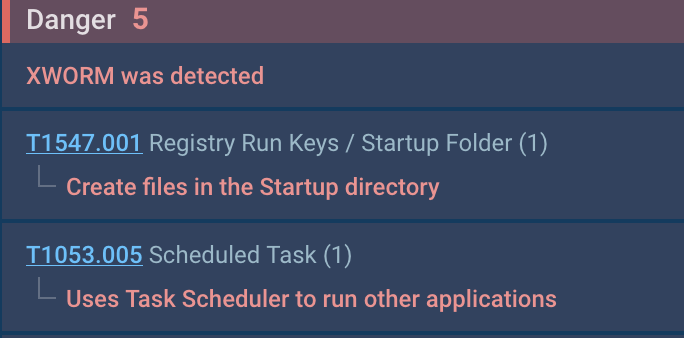 Figure 3: XWorm’s routines on the infected method.
Figure 3: XWorm’s routines on the infected method.
MITRE T1547.001: XWorm extra its shortcut to the Startup directory.
MITRE T1053.005: It utilized the activity scheduler to restart itself with elevated privileges, as indicated by the “/RL Maximum” parameter.
MITRE T1074.001: The program was installed in the General public directory.
MITRE T1571: The malware tried out to hook up to a remote server, but no response was been given.
XWorm’s unsuccessful attempt to evade sandbox investigation
Since the initial assessment report was a number of times old, the group decided to run the sample by means of the sandbox when again to verify for new things to do.
However, following launch, the malware crashed just about right away. A quick investigation created it obvious that the sample now queried a particular services to ascertain if it was functioning in a virtual sandbox.
Primarily, XWorm builders executed an evasion method, which caused the destructive application to shut down as before long as it sensed a virtualized ecosystem.
To overcome this, the group enabled Household Proxy in the sandbox options. This function replaces the virtual machine’s datacenter IP handle with 1 from an genuine ISP, generating the malware assume it is managing on a serious user’s equipment.
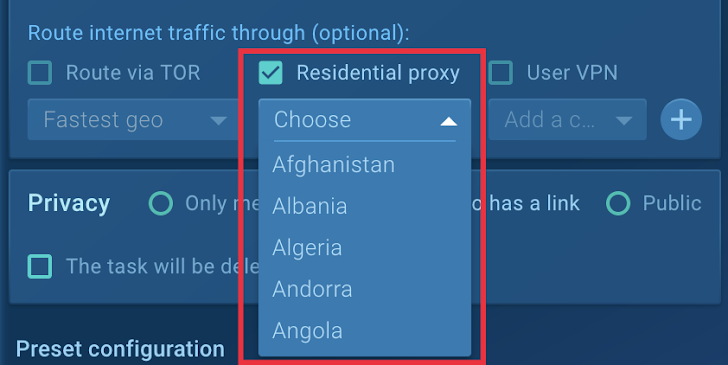 Determine 4: Household Proxy provides IP addresses from several
Determine 4: Household Proxy provides IP addresses from several
Right after rerunning the sample with Residential Proxy enabled, XWorm was effectively executed and started its activity.
Malware AnalysisAnalyze This Sample and Far more with ANY.Run
Sign up and get Fast entry to evaluate this sample, and any other, on ANY.Operate. You should not overlook out on the best instrument to understand and battle threats.
Make Totally free Account
On best of that, with the enable of the MITM proxy element, it was attainable to extract the info transmitted by XWorm to Telegram (MITRE T1102). The information bundled: the malware’s variation (XWorm V3.1), the machine’s username, the OS variation, and likely the victim’s hash.
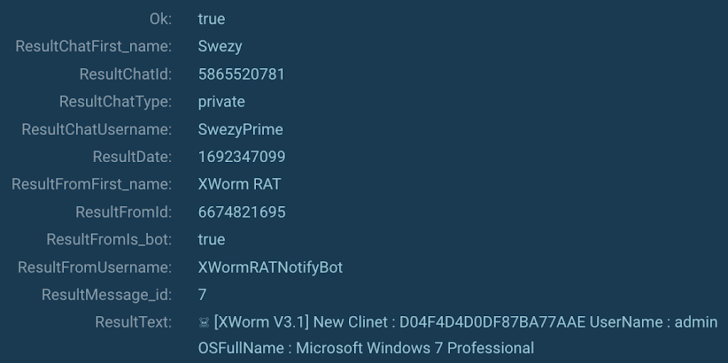 Figure 5: XWorm collected technique facts (MITRE T1082).
Figure 5: XWorm collected technique facts (MITRE T1082).
Static assessment of the new XWorm variant
Immediately after gathering all the important information and facts provided by the sandbox, the analysts commenced the static analysis section of their study. The 1st phase was to load the sample into Detect it Effortless (DIE), an marketplace standard for initial malware evaluation. The plan quickly identified that it was a .NET variation of XWorm.
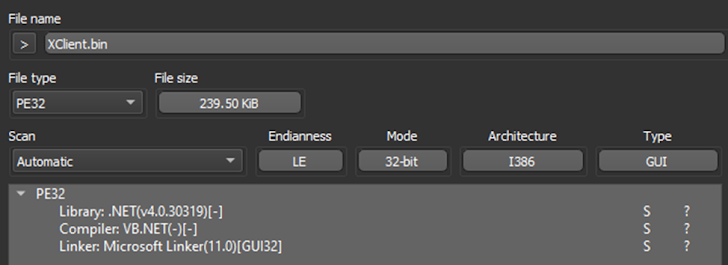 Determine 6: DIE provided an perception into the malware’s compiler.
Determine 6: DIE provided an perception into the malware’s compiler.
From there, the only rational action for the team was to open the file in dnSpy, a .NET debugger, which promptly disclosed that the binary was subject to hefty obfuscation. Nonetheless, DIE failed to figure out the packer even using Heuristic scanning.
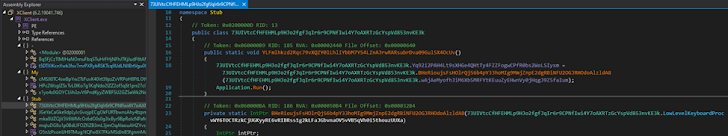 Determine 7: The XWorm’s code turned out to be obfuscated (MITRE T1027).
Determine 7: The XWorm’s code turned out to be obfuscated (MITRE T1027).
Utilizing de4dot, a .NET deobfuscator and unpacker, also did not have any influence.
More of XWorm’s evasion and persistence tactics
Further more investigation of the destructive binary allowed the crew to uncover extra pieces of the puzzle. Precisely, a variety of further mechanics utilized by the malware had been uncovered:
Virtualization detection: XWorm utilized the WMI question “Pick * from Get32_ComputerSystem” to look at for VmWare or VirtualBox environments.
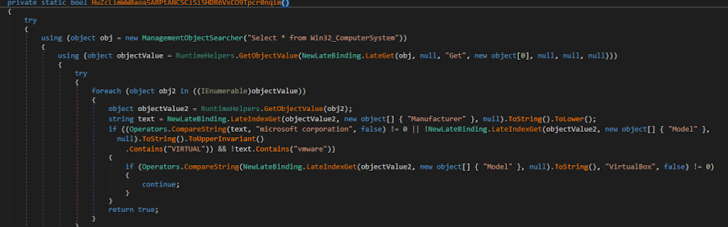 Figure 8: The malware exploited Windows Administration Instrumentation (MITRE T1047).
Figure 8: The malware exploited Windows Administration Instrumentation (MITRE T1047).
Debugger detection: It also ran the CheckRemoteDebuggerPresent API function to see if it was becoming debugged.
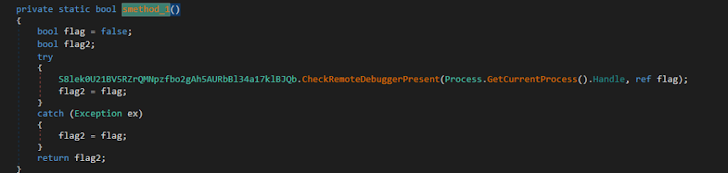 Figure 9: Xworm tried to evade debugger assessment.
Figure 9: Xworm tried to evade debugger assessment.
Sandboxie detection: The binary scanned the procedure to see if the SbieDll.dll library was loaded.
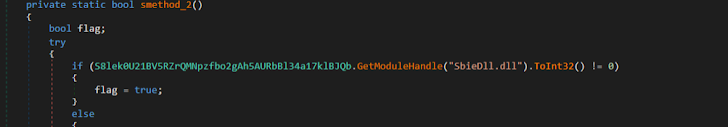 Figure 10: SbieDll.dll is linked with Sandboxie, a sandbox-centered isolation application.
Figure 10: SbieDll.dll is linked with Sandboxie, a sandbox-centered isolation application.
Datacenter IP verify: Xworm queried the equipment to establish if it was hosted in a details heart.
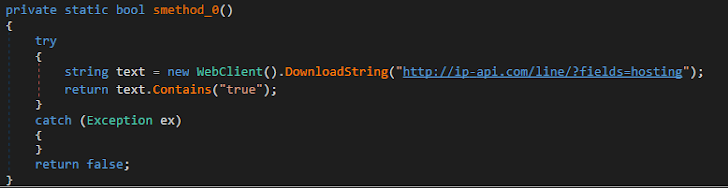 Determine 11: The malware’s IP scanning describes the explanation behind its first crash.
Determine 11: The malware’s IP scanning describes the explanation behind its first crash.
Persistence: XWorm employed the registry and the job scheduler to set up a persistent existence on the program.
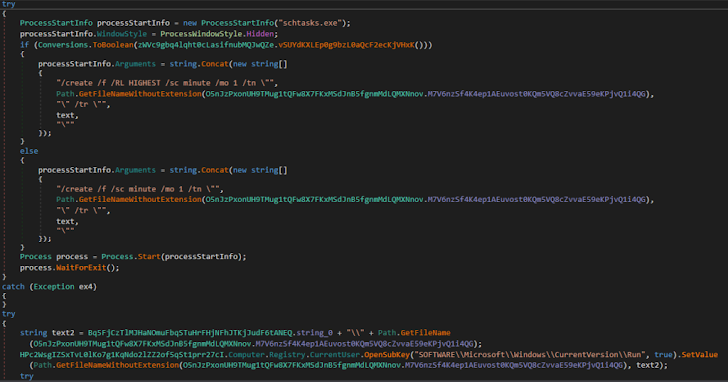 Figure 12: The code uncovered the malware’s potential to modify the registry.
Figure 12: The code uncovered the malware’s potential to modify the registry.
Extraction of XWorm’s configuration
Up coming, the analysts identified a constructor that appeared like a block containing settings. They applied a operate to reassign some of its fields. The malware initially computed an MD5 hash from a value in the presumed settings part.
It then copied the attained value 2 times into a short-term array, but due to an off-by-1 mistake, the MD5 was not currently being copied totally two times. The workforce used the received array as a key to decrypt the incoming base64 strings making use of AES in ECB method.
They also found that the area applied was a mutex. The total procedure is described in detail in ANY.RUN’s blog post “XWorm: Specialized Evaluation of a New Malware Variation.”
XWorm’s configuration
The entire configuration of XWorm’s new variant is as follows:
Host
6[.]tcp.eu.ngrok[.]io
Port
13394
AES essential
Slaves!-.!2Swezy999!(xxx
Splitter
Xwormmm
Sleep time
3
USB drop file
USB.exe
Mutex
Lz8qftMH08V7f1rq
Log file
%temp%\Log.tmp
Telegram token
6674821695:AAExQsr6_hmXk6hz7CN4kMSi9cs9y86daYM
Telegram chat id
5865520781
Summary
Getting configurations of the hottest malware is important but time-consuming. To make it more economical, you can operate your samples by means of the ANY.Operate sandbox to access the necessary data in seconds.
Examine it by yourself using the XWorm sample. As well as, ANY.Run gives a 14-working day cost-free trial of its best plan to security teams to support them exam the abilities of the services.
Observed this article intriguing? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through a lot more exclusive content we write-up.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Earth Lusca’s New SprySOCKS Linux Backdoor Targets Government Entities
Earth Lusca’s New SprySOCKS Linux Backdoor Targets Government Entities