Google has introduced plans to increase a new aspect in the upcoming variation of its Chrome web browser to inform buyers when an extension they have mounted has been taken out from the Chrome Web Keep.
The attribute, established for release together with Chrome 117, allows consumers to be notified when an incorporate-on has been unpublished by a developer, taken down for violating Chrome Web Store plan, or marked as malware.
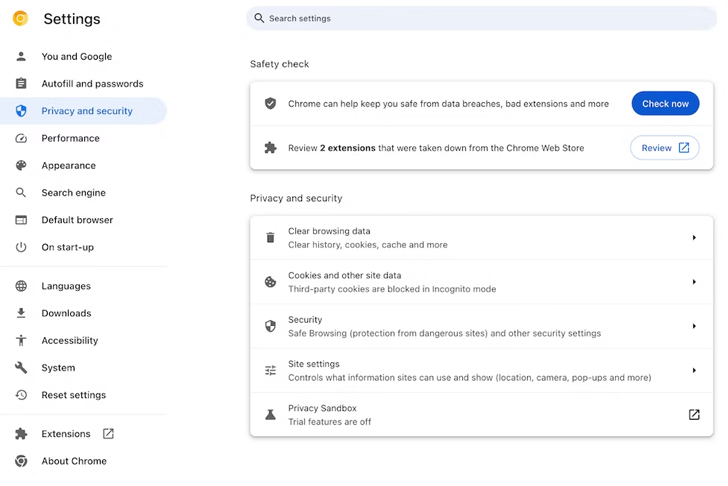
The tech huge said it intends to highlight these extensions beneath a “Basic safety check” classification in the “Privacy and security” portion of the browser options page.
“When a user clicks ‘Review,’ they will be taken to their extensions and supplied the preference to either remove the extension or cover the warning if they wish to maintain the extension set up,” Oliver Dunk, a developer relations engineer for Chrome extensions, said.

“As in past versions of Chrome, extensions marked as malware are automatically disabled.”
The growth comes as the organization mentioned it is likely to routinely upgrade all https:// URL navigations to https:// even when end users simply click on a link that explicitly declares https://. The feature is at the moment becoming examined in Chrome 115, and is envisioned to be rolled out soon.
Google also said it will also clearly show a warning commencing in mid-September 2023 when people endeavor to obtain substantial-risk documents even though on an insecure relationship.
“Downloaded documents can have malicious code that bypasses Chrome’s sandbox and other protections, so a network attacker has a exceptional possibility to compromise your laptop when insecure downloads take place,” the Chromium staff claimed.

“Except HTTPS-Very first Mode is enabled, Chrome will not exhibit warnings when insecurely downloading information like visuals, audio, or video clip, as these file varieties are somewhat protected.”
Some of the other features that are in the pipeline include enabling HTTPS-Initially Method by default in Incognito Manner for a extra protected browsing working experience and instantly turning the setting on for users who seldom use HTTP.
Consumers can permit HTTPS-Initially Mode by enabling “Normally use protected connections” in Chrome security settings (chrome://settings/security).
The updates also stick to Google’s proposals to include guidance for quantum-resistant encryption algorithms in the Chrome browser, starting with edition 116.
Discovered this short article interesting? Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through a lot more distinctive content material we submit.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 NoFilter Attack: Sneaky Privilege Escalation Method Bypasses Windows Security
NoFilter Attack: Sneaky Privilege Escalation Method Bypasses Windows Security