Cybersecurity scientists have discovered a new cryptojacking campaign that employs vulnerable drivers to disable acknowledged security remedies (EDRs) and thwart detection in what is actually termed a Deliver Your Own Susceptible Driver (BYOVD) attack.
Elastic Security Labs is monitoring the marketing campaign under the name REF4578 and the main payload as GHOSTENGINE. Prior exploration from Chinese cybersecurity organization Antiy Labs has codenamed the action as Hidden SHOVEL.
“GHOSTENGINE leverages vulnerable motorists to terminate and delete identified EDR agents that would possible interfere with the deployed and nicely-identified coin miner,” Elastic scientists Salim Bitam, Samir Bousseaden, Terrance DeJesus, and Andrew Pease said.
“This campaign included an uncommon amount of complexity to assure both the installation and persistence of the XMRig miner.”
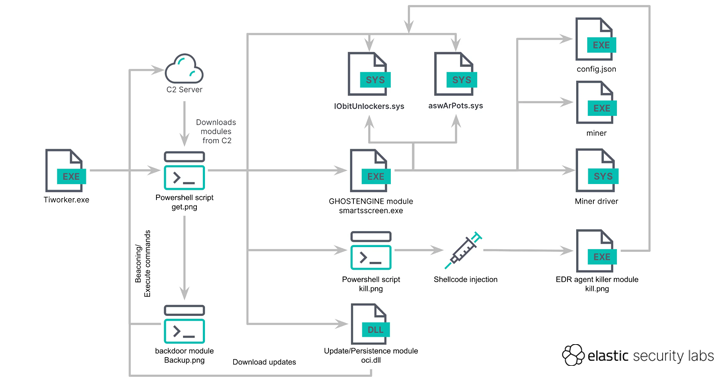
It all starts off with an executable file (“Tiworker.exe”), which is used to operate a PowerShell script that retrieves an obfuscated PowerShell script that masquerades as a PNG picture (“get.png”) to fetch supplemental payloads from a command-and-manage (C2) server.
These modules — aswArPot.sys, IObitUnlockers.sys, curl.exe, smartsscreen.exe, oci.dll, backup.png, and kill.png — are launched on the infected host right after downloading them above HTTP from both the configured C2 server or a backup server in case the domains are unavailable. It also incorporates an FTP-centered fallback mechanism.
On top of that, the malware tries to disable Microsoft Defender Antivirus, distinct various Windows function log channels, and make sure that the C: quantity has at minimum 10 MB of absolutely free space to download data files, which are then stashed in the C:WindowsFonts folder.
“If not, it will try out to delete large information from the system right before on the lookout for a different appropriate quantity with sufficient space and making a folder beneath $RECYCLE.BINFonts,” the scientists claimed.
The PowerShell script is also created to make a few scheduled responsibilities on the method to operate a malicious DLL every single 20 minutes, start alone by implies of a batch script every hour, and execute smartsscreen.exe every 40 minutes.

The core payload of the attack chain is smartsscreen.exe (aka GHOSTENGINE), whose primary goal is to deactivate security procedures employing the vulnerable Avast driver (“aswArPot.sys”), finish original infection, and execute the miner.
The security agent binary is then deleted by means of yet another vulnerable driver from IObit (“iobitunlockers.sys”), pursuing which the XMRig client mining software is downloaded from the C2 server and executed.
The DLL file is made use of to be certain the persistence of the malware and obtain updates from the C2 servers by fetching the get.png script and executing it, though the “backup.png” Powershell script functions as a backdoor to enable remote command execution on the system.
In what has been interpreted as a redundancy evaluate, the PowerShell script “get rid of.png” has similar abilities as smartsscreen.exe to delete security agent binaries by injecting and loading an executable file into memory.
The improvement comes as the Uptycs Risk Investigation Workforce found out a large-scale, ongoing operation given that January 2024 that exploits known flaws in the Log4j logging utility (e.g., CVE-2021-44228) to supply an XMRig miner onto the focused hosts.
“Subsequent to compromising a sufferer machine, it initiated speak to with a URL to fetch a shell script for the deployment of the XMRig miner, or alternatively, in choose occasions, it disseminated Mirai or Gafgyt malware,” security researcher Shilpesh Trivedi explained.
A the vast majority of the impacted servers are situated in China, adopted by Hong Kong, Netherlands, Japan, the U.S., Germany, South Africa, and Sweden.
BYOVD and Other Techniques to Undermine Security Mechanisms
BYOVD is an ever more well-liked technique whereby a danger actor provides a acknowledged-susceptible signed driver, loads it into the kernel, and exploits it to accomplish privileged actions, often with an aim to disarm security processes and enable them to function stealthily.
“Motorists run at ring , the most privileged stage of the operating system,” Israeli cybersecurity agency Cymulate notes. “This grants them direct access to critical memory, CPU, I/O operations, and other essential means. In the case of BYOVD, the attack is designed to load a susceptible driver to even further the attack.”
Though Microsoft has deployed the Susceptible Driver Blocklist by default starting in Windows 11 22H2, the listing is only up-to-date only as soon as or twice a 12 months, necessitating that buyers manually update it periodically for exceptional defense.
The actual scope of the campaign continues to be unfamiliar and it can be at the moment not obvious who is behind it. On the other hand, the unconventional sophistication powering what appears to be a clear-cut illicit cryptocurrency mining attack bears observe.

The disclosure also follows the discovery of a novel strategy called EDRaser that requires benefit of flaws in Microsoft Defender (CVE-2023-24860 and CVE-2023-36010) to remotely delete access logs, Windows function logs, databases, and other information.
The issue, which also impacts Kaspersky, stems from the truth that both equally the security courses use byte signatures to detect malware, consequently enabling a menace actor to implant malware signatures into legit information and fool the tools into imagining that they are malicious, SafeBreach said.
The cybersecurity firm has individually uncovered a inventive exploit to get close to security protections made available by Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR and weaponize it to deploy a reverse shell and ransomware, proficiently repurposing it into a rogue offensive software.

At its main, the bypass tends to make it probable to load a vulnerable driver (“rtcore64.sys”) by using a BYOVD attack and tamper with the solution to protect against a authentic administrator from getting rid of the application and ultimately insert destructive code into just one of its processes, granting the threat actor superior privileges although remaining undetected and persistent.
“The logic driving the detection procedures of a security item should be closely guarded,” security researcher Shmuel Cohen explained very last month. “By supplying attackers entry to this sensitive detection logic through the solution’s information files, they are substantially a lot more likely to be ready to engineer a way about it.”
A further novel process is HookChain, which, as Brazilian security researcher Helvio Carvalho Junior, consists of combining IAT hooking, dynamic procedure service quantities (SSN) resolution, and oblique method phone calls to escape monitoring and regulate mechanisms carried out by security program in the consumer mode, especially in the NTDLL.dll library.
“HookChain is able of redirecting the execution movement of all key Windows subsystems, this sort of as kernel32.dll, kernelbase.dll, and person32.dll,” Carvalho Junior stated in a freshly printed paper.
“This usually means that, after deployed, HookChain guarantees that all API phone calls in just the context of an software are carried out transparently, fully steering clear of detection by [Endpoint detection and response software].”
Identified this write-up interesting? Adhere to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to study more unique articles we write-up.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 MS Exchange Server Flaws Exploited to Deploy Keylogger in Targeted Attacks
MS Exchange Server Flaws Exploited to Deploy Keylogger in Targeted Attacks