Threat actors driving the Akira ransomware team have extorted roughly $42 million in illicit proceeds immediately after breaching the networks of extra than 250 victims as of January 1, 2024.
“Since March 2023, Akira ransomware has impacted a broad variety of businesses and critical infrastructure entities in North The us, Europe, and Australia,” cybersecurity organizations from the Netherlands and the U.S., alongside with Europol’s European Cybercrime Centre (EC3), stated in a joint inform.
“In April 2023, adhering to an initial concentrate on Windows programs, Akira risk actors deployed a Linux variant targeting VMware ESXi digital devices.”
The double-extortion team has been noticed applying a C++ variant of the locker in the early phases, just before shifting to a Rust-dependent code as of August 2023. It is really worth noting that the e-crime actor is absolutely unique from the Akira ransomware loved ones that was energetic in 2017.
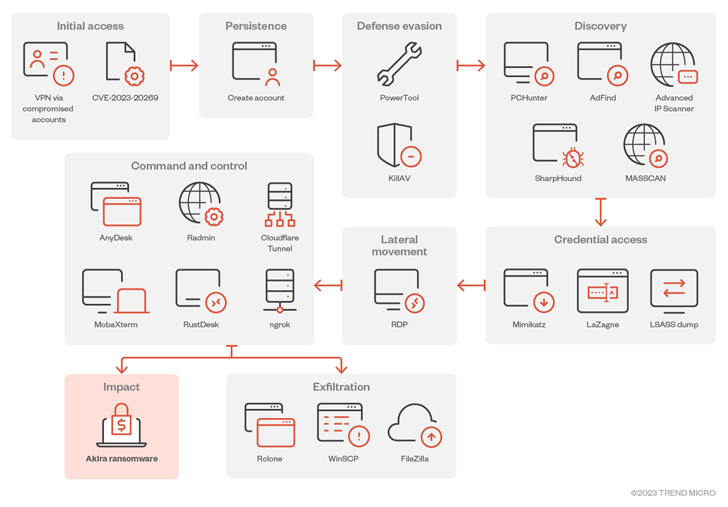
Initial obtain to focus on networks is facilitated by signifies of exploiting recognised flaws in Cisco appliances (e.g., CVE-2020-3259 and CVE-2023-20269).
Alternate vectors include the use of Distant Desktop Protocol (RDP), spear-phishing, valid credentials, and digital non-public network (VPN) providers lacking in multi-issue authentication (MFA) protections.

Akira actors are also known to leverage several strategies to set up persistence by producing a new domain account on the compromised process, as nicely as evade detection by abusing the Zemana AntiMalware driver to terminate antivirus-connected procedures by means of what is actually termed a Deliver Your Have Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) attack.
To help in privilege escalation, the adversary depends on credential scraping applications like Mimikatz and LaZagne, although Windows RDP is used to shift laterally inside the victim’s network. Facts exfiltration is completed via FileZilla, WinRAR, WinSCP, and RClone.
“Akira ransomware encrypts focused programs applying a hybrid encryption algorithm that brings together Chacha20 and RSA,” Trend Micro said in an investigation of the ransomware published in October 2023.
“Additionally, the Akira ransomware binary, like most present day ransomware binaries, has a attribute that lets it to inhibit program restoration by deleting shadow copies from the influenced procedure.”
Blockchain and source code facts indicates that Akira ransomware team is most likely affiliated with the now-defunct Conti ransomware gang. A decryptor for Akira was launched by Avast final July, but it truly is extremely probable the shortcomings have because been plugged.
Akira’s mutation to concentrate on Linux enterprise environments also follows equivalent moves by other set up ransomware families such as LockBit, Cl0p, Royal, Monti, and RTM Locker.
LockBit’s Struggles to Arrive Again
The disclosure comes as Development Micro discovered that the sweeping regulation enforcement takedown of the prolific LockBit gang earlier this February has experienced a substantial operational and reputational impact on the group’s potential to bounce again, prompting it to put up outdated and fake victims on its new facts leak internet site.
“LockBit was a single of the most prolific and widely utilized RaaS strains in procedure, with likely hundreds of affiliate marketers, which includes several affiliated with other popular strains,” Chainalysis mentioned in February.
The blockchain analytics business said it uncovered cryptocurrency trails connecting a LockBit administrator to a journalist dependent in Sevastopol identified as Colonel Cassad, who has a historical past of soliciting donations for Russian militia group operations in the sanctioned jurisdictions of Donetsk and Luhansk following the onset of the Russo-Ukrainian war in 2022.
It truly is truly worth pointing out that Cisco Talos, in January 2022, connected Colonel Cassad (aka Boris Rozhin) to an anti-Ukraine disinformation marketing campaign orchestrated by the Russian state-sponsored group recognized as APT28.
“Adhering to the procedure, LockBitSupp [the alleged leader of LockBit] appears to be making an attempt to inflate the evident victim rely whilst also concentrating on posting victims from international locations whose legislation enforcement agencies participated in the disruption,” Craze Micro reported in a recent deep dive.
“This is probably an try to boost the narrative that it would appear back again much better and target people liable for its disruption.”
In an job interview with Recorded Upcoming Information very last month, LockBitSupp acknowledged the short-expression drop in revenue, but promised to make improvements to their security actions and “work as extensive as my coronary heart beats.”

“Track record and belief are key to attracting affiliate marketers, and when these are shed, it truly is harder to get men and women to return. Operation Cronos succeeded in striking against one particular ingredient of its company that was most critical: its model,” Trend Micro said.
Agenda Returns with an Updated Rust Variation
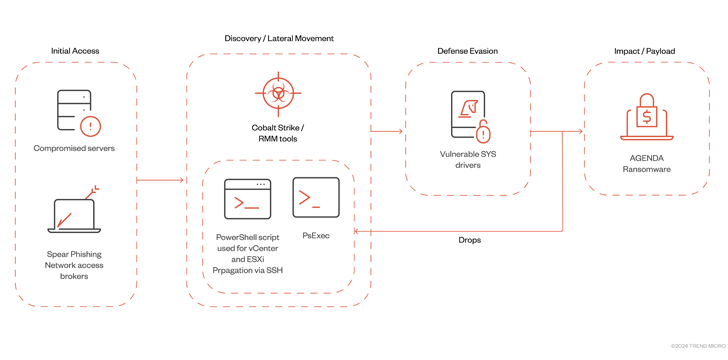
The progress also follows the Agenda ransomware group’s (aka Qilin and Water Galura) use of an updated Rust variant to infect VMWare vCenter and ESXi servers by way of Remote Monitoring and Administration (RMM) resources and Cobalt Strike.
“The Agenda ransomware’s capacity to distribute to digital device infrastructure shows that its operators are also increasing to new targets and systems,” the cybersecurity business stated.
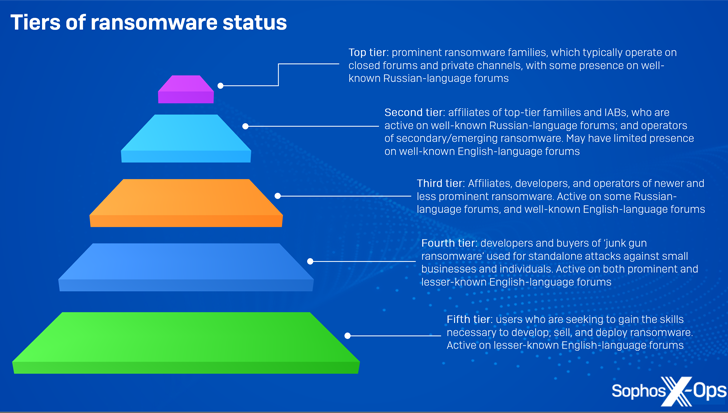
Even as a refreshing crop of ransomware actors proceeds to energize the risk landscape, it really is also turning out to be clearer that “crude, low cost ransomware” marketed on the cybercrime underground is becoming place to use in serious-environment attacks, enabling reduced-tier particular person danger actors to make significant gain with no acquiring to be a element of a properly-structured group.
Curiously, a greater part of these types are readily available for a one, just one-off value starting off from as very low as $20 for a single create, even though a handful of some others this sort of as HardShield and RansomTuga are presented at no added price.
“Absent from the sophisticated infrastructure of contemporary ransomware, junk-gun ransomware allows criminals to get in on the motion cheaply, conveniently, and independently,” Sophos mentioned, describing it as a “rather new phenomenon” that more lowers the price tag of entry.
“They can goal smaller organizations and persons, who are not likely to have the resources to defend them selves or reply efficiently to incidents, devoid of supplying anyone else a slash.”
Uncovered this report interesting? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through far more special content we publish.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Hackers Target Middle East Governments with Evasive “CR4T” Backdoor
Hackers Target Middle East Governments with Evasive “CR4T” Backdoor