Cybersecurity scientists have disclosed several critical security flaws in the TorchServe tool for serving and scaling PyTorch designs that could be chained to obtain remote code execution on impacted units.
Israel-based mostly runtime application security organization Oligo, which created the discovery, has coined the vulnerabilities ShellTorch.
“These vulnerabilities […] can guide to a comprehensive chain Distant Code Execution (RCE), leaving countless thousands of expert services and stop-buyers — together with some of the world’s greatest providers — open up to unauthorized obtain and insertion of malicious AI versions, and potentially a entire server takeover,” security researchers Idan Levcovich, Male Kaplan, and Gal Elbaz explained.

The checklist of flaws, which have been addressed in version .8.2, is as follows –
- No CVE – Unauthenticated Management Interface API Misconfiguration (…)
- CVE-2023-43654 (CVSS rating: 7.2) – A remote server-aspect ask for forgery (SSRF) that prospects to remote code execution.
- CVE-2022-1471 (CVSS rating: 9.9) – Use of an insecure version of the SnakeYAML open up-resource library that allows for unsafe deserialization of Java objects
Productive exploitation of the aforementioned flaws could allow for an attacker to deliver a ask for to upload a malicious design from an actor-managed tackle, leading to arbitrary code execution.
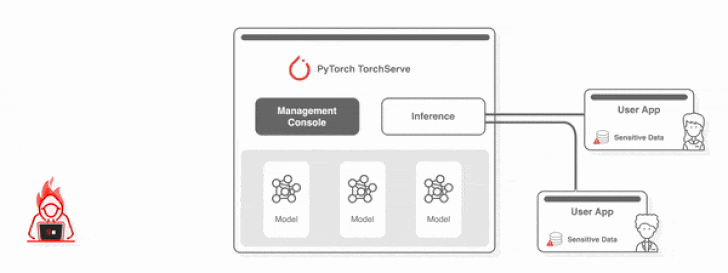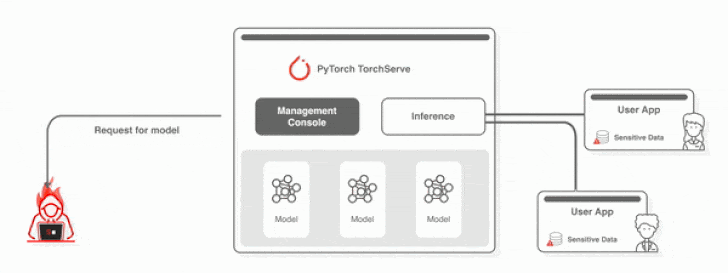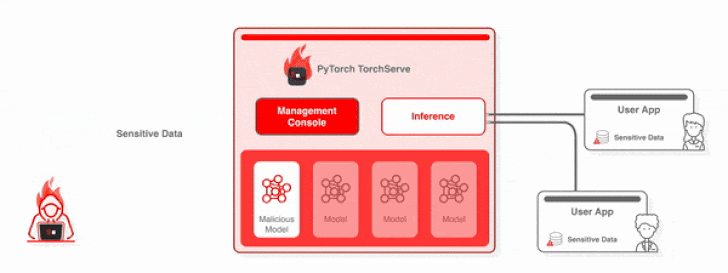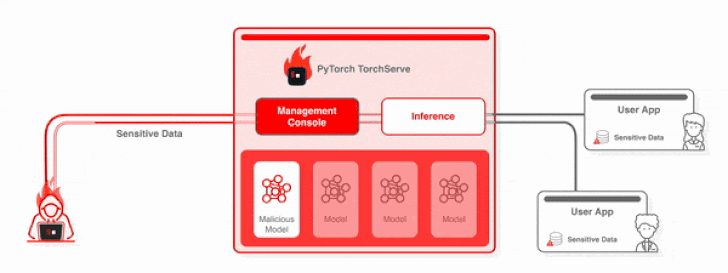
Set in other words, an attacker who can remotely access the administration server can also add a destructive design, which enables code execution without the need of demanding any authentication on any default TorchServe server.
Even far more troublingly, the shortcomings could be chained with CVE-2022-1471 to pave the way for code execution and whole takeover of exposed situations.

“AI styles can include a YAML file to declare their preferred configuration, so by uploading a product with a maliciously crafted YAML file, we ended up capable to bring about an unsafe deserialization attack that resulted in code execution on the machine,” the researchers stated.
The severity of the issues has prompted Amazon Web Providers (AWS) to issue an advisory urging buyers working with PyTorch inference Deep Understanding Containers (DLC) 1.13.1, 2.., or 2..1 in EC2, EKS, or ECS launched prior to September 11, 2023, update to TorchServe edition .8.2.
“Making use of the privileges granted by these vulnerabilities, it is attainable to look at, modify, steal, and delete AI products and delicate data flowing into and from the target TorchServe server,” the researchers said.
“Creating these vulnerabilities even a lot more dangerous: when an attacker exploits the design serving server, they can entry and alter delicate info flowing in and out from the focus on TorchServe server, harming the trust and credibility of the software.”
Identified this report fascinating? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through more special material we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Over 3 Dozen Data-Stealing Malicious npm Packages Found Targeting Developers
Over 3 Dozen Data-Stealing Malicious npm Packages Found Targeting Developers