Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered an “implementation vulnerability” that has created it attainable to reconstruct encryption keys and decrypt knowledge locked by Rhysida ransomware.
The findings had been published last 7 days by a group of researchers from Kookmin University and the Korea Internet and Security Company (KISA).
“By way of a thorough assessment of Rhysida Ransomware, we determined an implementation vulnerability, enabling us to regenerate the encryption critical utilised by the malware,” the scientists reported.
The advancement marks the 1st prosperous decryption of the ransomware pressure, which initially designed its visual appeal in May 2023. A restoration tool is remaining dispersed via KISA.

The review is also the newest to realize information decryption by exploiting implementation vulnerabilities in ransomware, immediately after Magniber v2, Ragnar Locker, Avaddon, and Hive.
Rhysida, which is known to share overlaps with a different ransomware crew termed Vice Society, leverages a tactic identified as double extortion to use pressure on victims into spending up by threatening to release their stolen data.
An advisory revealed by the U.S. authorities in November 2023 identified as out the menace actors for staging opportunistic assaults focusing on training, production, facts technology, and government sectors.
A extensive examination of the ransomware’s interior workings has discovered its use of LibTomCrypt for encryption as very well as parallel processing to velocity up the method. It has also been discovered to put into action intermittent encryption (aka partial encryption) to evade detection by security remedies.
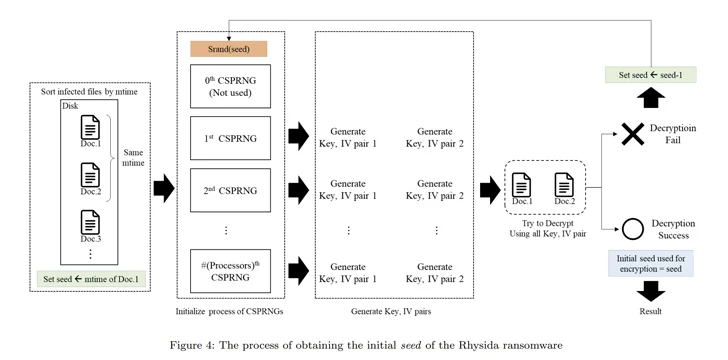
“Rhysida ransomware uses a cryptographically protected pseudo-random quantity generator (CSPRNG) to make the encryption critical,” the scientists mentioned. “This generator makes use of a cryptographically protected algorithm to crank out random figures.”
Exclusively, the CSPRNG is primarily based on the ChaCha20 algorithm presented by the LibTomCrypt library, with the random selection generated also correlated to the time at which Rhysida ransomware is jogging.

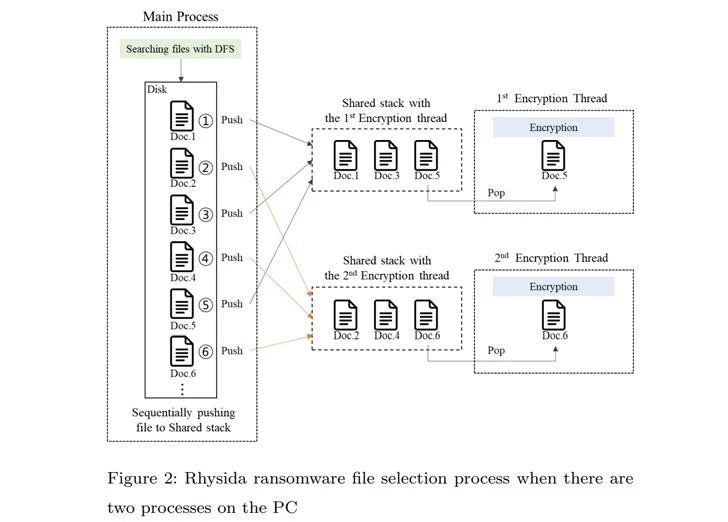
That is not all. The principal system of Rhysida ransomware compiles a listing of documents to be encrypted. This checklist is subsequently referenced by numerous threads made to at the same time encrypt the data files in a particular buy.
“In the encryption procedure of the Rhysida ransomware, the encryption thread generates 80 bytes of random numbers when encrypting a single file,” the scientists noted. “Of these, the very first 48 bytes are applied as the encryption crucial and the [initialization vector].”
Working with these observations as reference factors, the scientists explained they were ready to retrieve the first seed for decrypting the ransomware, identify the “randomized” purchase in which the data files were being encrypted, and finally recover the facts without having acquiring to pay back a ransom.
“While these reports have a constrained scope, it is essential to acknowledge that particular ransomwares […] can be correctly decrypted,” the researchers concluded.
Uncovered this write-up intriguing? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through much more special information we put up.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 4 Ways Hackers use Social Engineering to Bypass MFA
4 Ways Hackers use Social Engineering to Bypass MFA