Cybersecurity researchers have identified a novel attack that employs stolen cloud qualifications to focus on cloud-hosted huge language model (LLM) services with the target of promoting obtain to other menace actors.
The attack strategy has been codenamed LLMjacking by the Sysdig Danger Research Workforce.
“Once original obtain was received, they exfiltrated cloud credentials and received accessibility to the cloud surroundings, exactly where they tried to accessibility neighborhood LLM styles hosted by cloud suppliers,” security researcher Alessandro Brucato explained. “In this instance, a nearby Claude (v2/v3) LLM model from Anthropic was focused.”
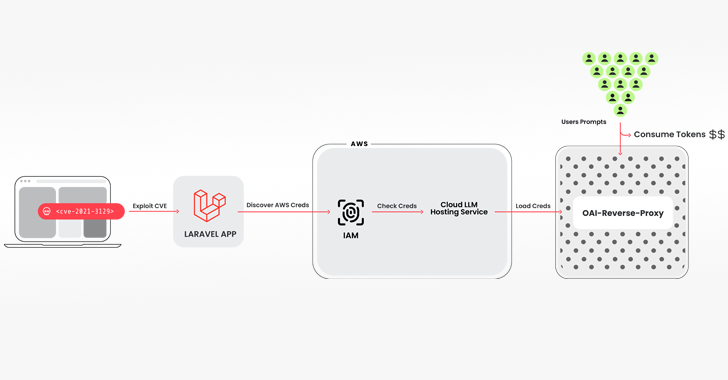
The intrusion pathway utilized to pull off the scheme entails breaching a program functioning a vulnerable version of the Laravel Framework (e.g., CVE-2021-3129), adopted by receiving keep of Amazon Web Products and services (AWS) credentials to access the LLM products and services.

Amid the tools used is an open up-resource Python script that checks and validates keys for a variety of choices from Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, Google Cloud Vertex AI, Mistral, and OpenAI, between others.
“No reputable LLM queries were being essentially operate throughout the verification phase,” Brucato discussed. “As a substitute, just enough was accomplished to determine out what the credentials had been capable of and any quotas.”
The keychecker also has integration with one more open-resource software referred to as oai-reverse-proxy that features as a reverse proxy server for LLM APIs, indicating that the risk actors are likely furnishing entry to the compromised accounts with out basically exposing the fundamental qualifications.
“If the attackers ended up collecting an inventory of beneficial credentials and wished to market obtain to the offered LLM types, a reverse proxy like this could allow them to monetize their efforts,” Brucato said.
Furthermore, the attackers have been noticed querying logging settings in a possible attempt to sidestep detection when making use of the compromised qualifications to operate their prompts.
The growth is a departure from attacks that concentration on prompt injections and model poisoning, as a substitute enabling attackers to monetize their obtain to the LLMs though the operator of the cloud account foots the monthly bill without their awareness or consent.

Sysdig claimed that an attack of this kind could rack up more than $46,000 in LLM use fees for each working day for the victim.
“The use of LLM products and services can be expensive, depending on the product and the quantity of tokens currently being fed to it,” Brucato said. “By maximizing the quota boundaries, attackers can also block the compromised group from employing versions legitimately, disrupting company operations.”
Businesses are recommended to permit comprehensive logging and watch cloud logs for suspicious or unauthorized action, as very well as make certain that powerful vulnerability administration processes are in location to avoid preliminary access.
Observed this article exciting? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through extra special content material we publish.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 New TunnelVision Attack Allows Hijacking of VPN Traffic via DHCP Manipulation
New TunnelVision Attack Allows Hijacking of VPN Traffic via DHCP Manipulation