Ransomware teams are significantly switching to remote encryption in their assaults, marking a new escalation in strategies adopted by monetarily determined actors to ensure the achievements of their campaigns.
“Firms can have countless numbers of personal computers connected to their network, and with remote ransomware, all it usually takes is 1 underprotected device to compromise the whole network,” Mark Loman, vice president of menace investigation at Sophos, explained.
“Attackers know this, so they hunt for that one’ weak spot’ — and most companies have at minimum one. Remote encryption is likely to keep a perennial issue for defenders.”
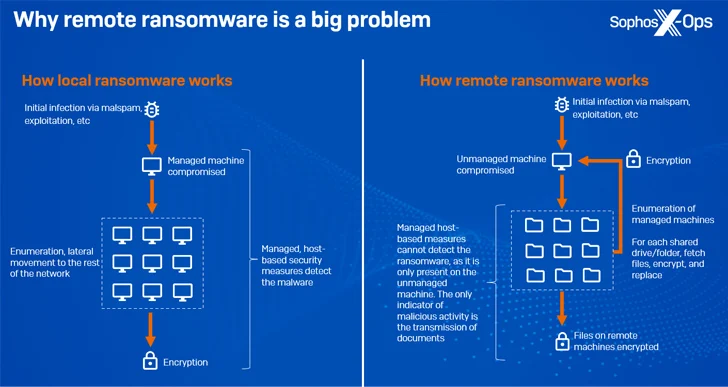
Remote encryption (aka distant ransomware), as the identify indicates, occurs when a compromised endpoint is applied to encrypt data on other units on the similar network.
Future WEBINAR Conquer AI-Powered Threats with Zero Have confidence in – Webinar for Security Specialists
Regular security steps won’t slash it in present day planet. It’s time for Zero Rely on Security. Protected your information like never ahead of.
Join Now
In October 2023, Microsoft discovered that all over 60% of ransomware attacks now involve malicious distant encryption in an effort to lower their footprint, with more than 80% of all compromises originating from unmanaged units.
“Ransomware households regarded to assistance distant encryption include Akira, ALPHV/BlackCat, BlackMatter, LockBit, and Royal, and it can be a method that is been all over for some time – as significantly back again as 2013, CryptoLocker was focusing on network shares,” Sophos explained.
A substantial benefit to this approach is that it renders process-dependent remediation actions ineffective and the managed equipment are unable to detect the destructive exercise considering that it is only current in an unmanaged unit.
The development arrives amid broader shifts in the ransomware landscape, with the danger actors adopting atypical programming languages, concentrating on beyond Windows methods, auctioning stolen facts, and launching assaults immediately after company hrs and at weekends to thwart detection and incident reaction initiatives.
Sophos, in a report published past week, highlighted the “symbiotic – but generally uneasy – relationship” between ransomware gangs and the media, as a way to not only entice interest, but also to manage the narrative and dispute what they check out as inaccurate protection.
This also extends to publishing FAQs and press releases on their information leak internet sites, even such as immediate quotes from the operators, and correcting errors designed by journalists. One more tactic is the use of catchy names and slick graphics, indicating an evolution of the professionalization of cyber crime.

“The RansomHouse group, for example, has a concept on its leak internet site specially aimed at journalists, in which it features to share data on a ‘PR Telegram channel’ in advance of it is formally published,” Sophos observed.
While ransomware teams like Conti and Pysa are recognised for adopting an organizational hierarchy comprising senior executives, procedure admins, builders, recruiters, HR, and lawful groups, there is evidence to propose that some have marketed chances for English writers and speakers on criminal discussion boards.
“Media engagement presents ransomware gangs with the two tactical and strategic positive aspects it permits them to use tension to their victims, even though also enabling them to condition the narrative, inflate their have notoriety and egos, and more ‘mythologize’ themselves,” the enterprise claimed.
Found this report exciting? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to study more distinctive written content we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Product Explained: Memcyco’s Real-Time Defense Against Website Spoofing
Product Explained: Memcyco’s Real-Time Defense Against Website Spoofing