Cybersecurity researchers are warning of “imposter packages” mimicking common libraries out there on the Python Deal Index (PyPI) repository.
The 41 malicious PyPI packages have been found to pose as typosquatted variants of genuine modules this kind of as HTTP, AIOHTTP, requests, urllib, and urllib3.
The names of the offers are as follows:
aio5, aio6, htps1, httiop, httops, httplat, httpscolor, httpsing, httpslib, httpsos, httpsp, httpssp, httpssus, httpsus, httpxgetter, httpxmodifier, httpxrequester, httpxrequesterv2, httpxv2, httpxv3, libhttps, piphttps, pohttp, requestsd, requestse, requestst, ulrlib3, urelib3, urklib3, urlkib3, urllb, urllib33, urolib3, xhttpsp
“The descriptions for these packages, for the most section, don’t hint at their malicious intent,” ReversingLabs researcher Lucija Valentić mentioned in a new writeup. “Some are disguised as real libraries and make flattering comparisons among their abilities and those people of known, genuine HTTP libraries.”
But in truth, they both harbor downloaders that act as a conduit to produce next-phase malware to infected hosts or information stealers that are developed to exfiltrate sensitive facts these as passwords and tokens.
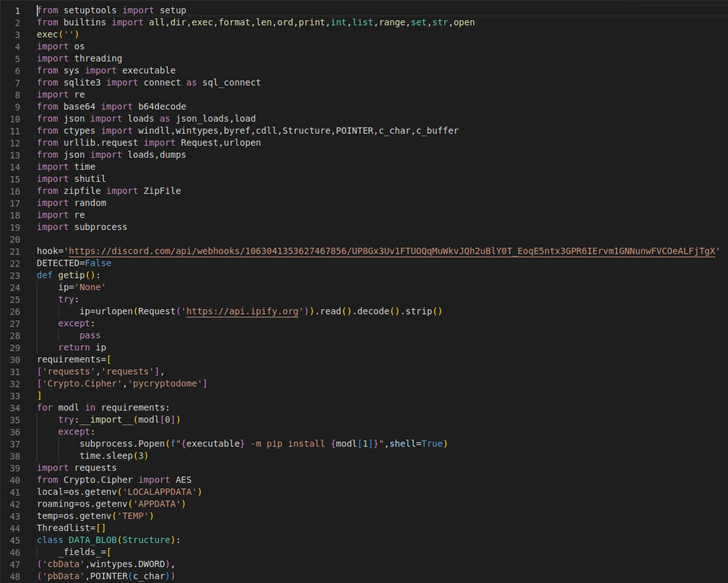
Fortinet, which also disclosed comparable rogue HTTP packages on PyPI before this 7 days, observed their means to start a trojan downloader that, in switch, consists of a DLL file (Rdudkye.dll) packing a assortment of functions.
The development is just the most up-to-date attempt by destructive actors to poison open up resource repositories like GitHub, npm, PyPI, and RubyGems to propagate malware to developer systems and mount source chain assaults.
The results come a day right after Checkmarx specific a surge in spam offers in the open resource npm registry that are developed to redirect victims to phishing hyperlinks.
“As with other supply chain attacks, malicious actors are counting on typosquatting creating confusion and counting on incautious builders to embrace destructive packages with related-sounding names by accident,” Valentić reported.
Found this posting fascinating? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to browse a lot more unique material we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Open Source Flaws Found in 84% of Codebases
Open Source Flaws Found in 84% of Codebases