The maintainers of the Python Bundle Index (PyPI) repository briefly suspended new user sign-ups next an inflow of malicious jobs uploaded as component of a typosquatting campaign.
It said “new job generation and new user registration” was quickly halted to mitigate what it reported was a “malware upload campaign.” The incident was solved 10 hrs afterwards, on March 28, 2024, at 12:56 p.m. UTC.
Software program offer chain security company Checkmarx stated the unknown menace actors driving flooding the repository focused developers with typosquatted versions of well-liked offers.
“This is a multi-stage attack and the malicious payload aimed to steal crypto wallets, sensitive facts from browsers (cookies, extensions facts, etcetera.), and several credentials,” scientists Yehuda Gelb, Jossef Harush Kadouri, and Tzachi Zornstain mentioned. “In addition, the malicious payload utilized a persistence system to survive reboots.”
The findings were being also corroborated independently by Mend.io, which famous that it detected much more than 100 malicious offers concentrating on equipment studying (ML) libraries these types of as Pytorch, Matplotlib, and Selenium.

The growth arrives as open up-resource repositories are more and more becoming an attack vector for threat actors to infiltrate enterprise environments.
Typosquatting is a effectively-documented attack approach in which adversaries upload offers with names intently resembling their respectable counterparts (e.g., Matplotlib vs. Matplotlig or tensorflow vs. tensourflow) in get to trick unsuspecting people into downloading them.
These misleading variants – totalling about 500 packages, per Test Place – have been identified to be uploaded from a special account setting up March 26, 2024, suggesting that the whole system was automatic.
“The decentralized character of the uploads, with just about every bundle attributed to a unique person, complicates efforts to cross-establish these malicious entries,” the Israeli cybersecurity corporation reported.
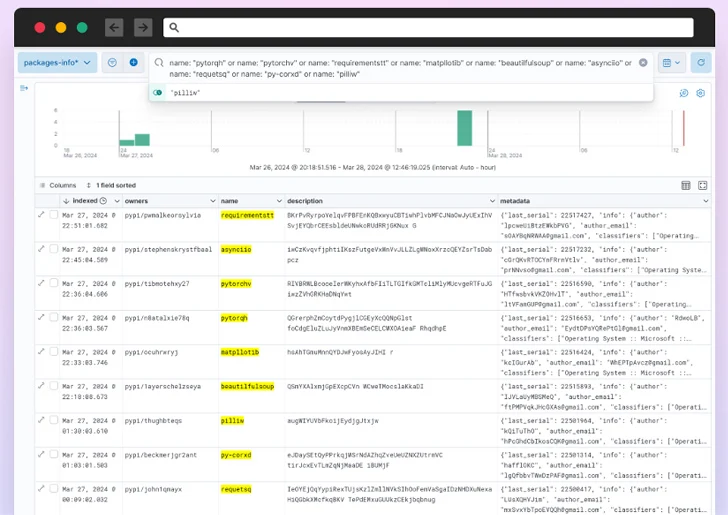
Cybersecurity firm Phylum, which has also been tracking the identical campaign, mentioned the attackers revealed –
- 67 variations of necessities
- 38 variants of Matplotlib
- 36 versions of requests
- 35 versions of colorama
- 29 versions of tensorflow
- 28 variants of selenium
- 26 variants of BeautifulSoup
- 26 variants of PyTorch
- 20 versions of pillow
- 15 versions of asyncio
The deals, for their component, test if the installer’s functioning process was Windows, and if so, progress to down load and execute an obfuscated payload retrieved from an actor-controlled domain (“funcaptcha[.]ru”).

The malware functions as a stealer, exfiltrating files, Discord tokens, as effectively as facts from web browsers and cryptocurrency wallets to the very same server. It additional attempts to download a Python script (“hvnc.py”) to the Windows Startup folder for persistence.
The growth as soon as yet again illustrates the escalating risk posed by software program source chain attacks, building it critical that developers scrutinize each individual 3rd-get together component to make sure that it safeguards in opposition to potential threats.
This is not the to start with time PyPI has resorted to these types of a evaluate. In May perhaps 2023, it briefly disabled user signal-ups soon after locating that the “volume of destructive buyers and destructive tasks staying produced on the index in the previous 7 days has outpaced our potential to respond to it in a timely vogue.”
PyPI suspended new user registrations a second-time final calendar year on December 27 for very similar factors. It was subsequently lifted on January 2, 2024.
Uncovered this short article fascinating? Adhere to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read additional exclusive material we publish.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Linux Version of DinodasRAT Spotted in Cyber Attacks Across Several Countries
Linux Version of DinodasRAT Spotted in Cyber Attacks Across Several Countries