The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Thursday included a security flaw impacting the Oracle WebLogic Server to the Regarded Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, citing evidence of active exploitation.
Tracked as CVE-2017-3506 (CVSS score: 7.4), the issue worries an working procedure (OS) command injection vulnerability that could be exploited to attain unauthorized obtain to vulnerable servers and get finish command.
“Oracle WebLogic Server, a product inside of the Fusion Middleware suite, is made up of an OS command injection vulnerability that lets an attacker to execute arbitrary code by using a specifically crafted HTTP request that contains a malicious XML doc,” CISA mentioned.

Even though the agency did not disclose the character of assaults exploiting the vulnerability, the China-centered cryptojacking group acknowledged as the 8220 Gang (aka H2o Sigbin) has a background of leveraging it due to the fact early last year to co-choose unpatched equipment into a crypto-mining botnet.
According to a the latest report posted by Development Micro, the 8220 Gang has been observed weaponizing flaws in the Oracle WebLogic server (CVE-2017-3506 and CVE-2023-21839) to start a cryptocurrency miner filelessly in memory by suggests of a shell or PowerShell script based on the working program specific.
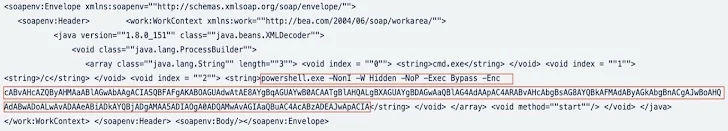
“The gang employed obfuscation approaches, such as hexadecimal encoding of URLs and working with HTTP about port 443, letting for stealthy payload supply,” security researcher Sunil Bharti claimed. “The PowerShell script and the ensuing batch file included advanced encoding, using surroundings variables to disguise destructive code inside seemingly benign script elements.”
In mild of the lively exploitation of CVE-2024-1086 and CVE-2024-24919, federal agencies are suggested to apply the hottest fixes by June 24, 2024, to safeguard their networks in opposition to potential threats.
Found this posting appealing? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through additional special articles we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Researchers Uncover RAT-Dropping npm Package Targeting Gulp Users
Researchers Uncover RAT-Dropping npm Package Targeting Gulp Users