North Korean nation-state actors affiliated with the Reconnaissance Common Bureau (RGB) have been attributed to the JumpCloud hack following an operational security (OPSEC) blunder that exposed their actual IP address.
Google-owned danger intelligence company Mandiant attributed the action to a threat actor it tracks less than the name UNC4899, which probable shares overlaps with clusters previously being monitored as Jade Sleet and TraderTraitor, a team with a heritage of putting blockchain and cryptocurrency sectors.
UNC4899 also overlaps with APT43, one more hacking crew involved with the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) that was unmasked earlier this March as conducting a sequence of strategies to obtain intelligence and siphon cryptocurrency from qualified corporations.
The adversarial collective’s modus operandi is characterized by the use of Operational Relay Bins (ORBs) working with L2TP IPsec tunnels alongside with commercial VPN vendors to disguise the attacker’s accurate place of origin, with professional VPN providers acting as the ultimate hop.
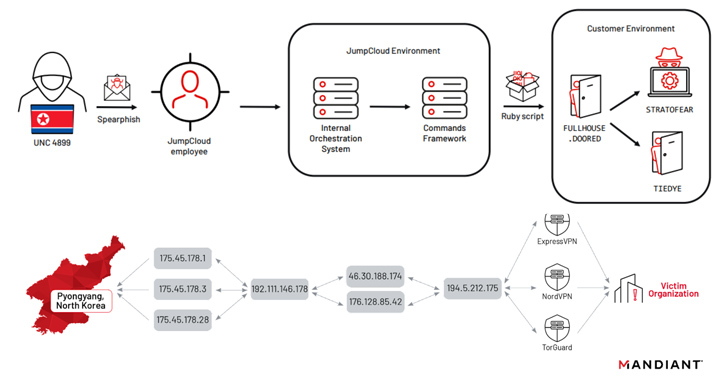
“There have been many instances in which DPRK risk actors did not hire this very last hop, or mistakenly did not utilize this when conducting steps on functions on the victim’s network,” the business mentioned in an analysis published Monday, incorporating it observed “UNC4899 connecting straight to an attacker-controlled ORB from their 175.45.178[.]/24 subnet.”
The intrusion directed from JumpCloud took area on June 22, 2023, as part of a complex spear-phishing marketing campaign that leveraged the unauthorized obtain to breach much less than 5 buyers and considerably less than 10 units in what’s known as a software package supply chain attack.
Mandiant’s findings are based on an incident reaction initiated in the aftermath of a cyber attack in opposition to a single of JumpCloud’s impacted consumers, an unnamed software program options entity, the setting up position getting a destructive Ruby script (“init.rb”) executed by means of the JumpCloud agent on June 27, 2023.
A noteworthy facet of the incident is its targeting of 4 Apple techniques functioning macOS Ventura versions 13.3 or 13.4.1, underscoring North Korean actors’ ongoing investment in honing malware specially tailor-made for the system in recent months.
“Preliminary entry was obtained by compromising JumpCloud and inserting destructive code into their instructions framework,” the firm spelled out. “In at the very least 1 instance, the destructive code was a light-weight Ruby script that was executed by way of the JumpCloud agent.”
The script, for its component, is engineered to obtain and execute a 2nd-stage payload named FULLHOUSE.DOORED, utilizing it as a conduit to deploy supplemental malware this kind of as STRATOFEAR and TIEDYE, immediately after which the prior payloads have been eradicated from the program in an attempt to go over up the tracks –
- FULLHOUSE.DOORED – A C/C++-dependent initial-phase backdoor that communicates making use of HTTP and arrives with assist for shell command execution, file transfer, file administration, and method injection
- STRATOFEAR – A second-stage modular implant that is mainly created to gather technique info as very well as retrieve and execute a lot more modules from a remote server or loaded from disk
- TIEDYE – A second-stage Mach-O executable that can converse with a distant server to run extra payloads, harvest primary technique information and facts, and execute shell instructions
TIEDYE is also claimed to exhibit similarities to RABBITHUNT, a backdoor penned in C++ that communicates by using a personalized binary protocol over TCP and which is able of reverse shell, file transfer, procedure development, and method termination.
“The marketing campaign targeting JumpCloud, and the earlier claimed DPRK offer chain compromise from previously this year which impacted the Investing Technologies X_TRADER application and 3CX Desktop Application software, exemplifies the cascading results of these functions to gain obtain to services providers in buy to compromise downstream victims,” Mandiant stated.
“The two functions have suspected ties to monetarily determined DPRK actors, suggesting that DPRK operators are employing provide chain TTPs to focus on find entities as component of improved endeavours to concentrate on cryptocurrency and fintech-connected assets.”
The improvement will come days soon after GitHub warned of a social engineering attack mounted by the TraderTraitor actor to trick staff members functioning at blockchain, cryptocurrency, online gambling, and cybersecurity firms into executing code hosted in a GitHub repository that relied on malicious deals hosted on npm.
The an infection chain has been found to leverage the destructive npm dependencies to down load an unidentified second-stage payload from an actor-managed area. The packages have considering that been taken down and the accounts suspended.
“The discovered offers, revealed in pairs, necessary installation in a certain sequence, subsequently retrieving a token that facilitated the down load of a closing malicious payload from a distant server,” Phylum explained in a new examination detailing the discovery of new npm modules made use of in the very same marketing campaign.
“The vast attack floor offered by these ecosystems is really hard to dismiss. It’s practically extremely hard for a developer in present-day entire world not to count on any open up-source offers. This fact is usually exploited by menace actors aiming to improve their blast radius for common distribution of malware, these kinds of as stealers or ransomware.”
Future WEBINARShield Towards Insider Threats: Master SaaS Security Posture Administration
Apprehensive about insider threats? We have obtained you protected! Be part of this webinar to check out simple approaches and the strategies of proactive security with SaaS Security Posture Management.
Join Today
Pyongyang has lengthy utilized cryptocurrency heists to gasoline its sanctioned nuclear weapons plan, even though simultaneously orchestrating cyber espionage assaults to accumulate strategic intelligence in aid of the regime’s political and nationwide security priorities.
“North Korea’s intelligence equipment possesses the overall flexibility and resilience to make cyber models dependent on the demands of the state,” Mandiant pointed out previous year. “Also overlaps in infrastructure, malware, and strategies, procedures and methods point out there are shared methods amongst their cyber functions.”
The Lazarus Group stays a prolific condition-sponsored risk actor in this regard, persistently mounting assaults that are intended to supply anything from remote entry trojans to ransomware to objective-developed backdoors and also demonstrating a readiness to shift practices and techniques to hinder evaluation and make their monitoring a lot more difficult.
This is exemplified by its capacity to not only compromise susceptible Microsoft Internet Data Assistance (IIS) web servers, but also use them as malware distribution facilities in watering hole assaults aimed at South Korea, according to the AhnLab Security Unexpected emergency Reaction Centre (ASEC).
“The danger actor is constantly utilizing vulnerability assaults for first access to unpatched devices,” ASEC reported. “It is a person of the most hazardous danger groups really lively worldwide.”
A 2nd RGB-backed group which is equally focused on amassing data on geopolitical occasions and negotiations impacting the DPRK’s interests is Kimsuky, which has been detected working with Chrome Distant Desktop to remotely commandeer hosts by now compromised by means of backdoors these kinds of as AppleSeed.
“The Kimsuky APT group is consistently launching spear-phishing attacks from Korean customers,” ASEC pointed out this month. “They typically hire techniques of malware distribution via disguised document information connected to e-mails, and consumers who open these information may shed management about their existing process.”
Observed this short article interesting? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to examine far more unique information we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Casbaneiro Banking Malware Goes Under the Radar with UAC Bypass Technique
Casbaneiro Banking Malware Goes Under the Radar with UAC Bypass Technique