
A earlier undocumented and generally undetected variant of a Linux backdoor known as BPFDoor has been noticed in the wild, cybersecurity business Deep Intuition explained in a complex report posted this week.
“BPFDoor retains its status as an extremely stealthy and tricky-to-detect malware with this most up-to-date iteration,” security researchers Shaul Vilkomir-Preisman and Eliran Nissan reported.
BPFDoor (aka JustForFun), initially documented by PwC and Elastic Security Labs in Might 2022, is a passive Linux backdoor associated with a Chinese danger actor called Pink Menshen (aka DecisiveArchitect or Crimson Dev 18), which is recognized to single out telecom vendors across the Center East and Asia because at the very least 2021.
The malware is precisely geared in the direction of setting up persistent remote obtain to compromised concentrate on environments for prolonged periods of time, with evidence pointing to the hacking crew operating the backdoor undetected for a long time.

BPFDoor will get its identify from the use of Berkeley Packet Filters (BPF) – a technology that can make it achievable to assess and filter network website traffic in Linux programs – for network communications and process incoming instructions.
In performing so, threat actors can penetrate a victim’s process and execute arbitrary code without being detected by firewalls, although concurrently filtering out avoidable data.
Deep Instinct’s conclusions arrive from a BPFDoor artifact that was uploaded to VirusTotal on February 8, 2023. As of writing, only 3 security sellers have flagged the ELF binary as destructive.
A single of the essential traits that make the new edition of BPFDoor even extra evasive is its removing of several tricky-coded indicators and as a substitute incorporating a static library for encryption (libtomcrypt) and a reverse shell for command-and-manage (C2) communication.
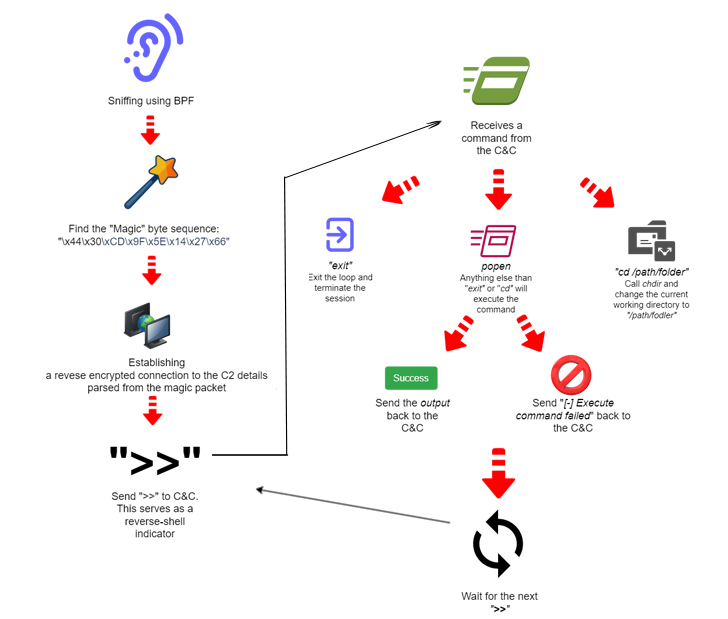
Upon start, BPFDoor is configured to disregard a variety of functioning technique alerts to protect against it from being terminated. It then allocates a memory buffer and generates a particular packet sniffing socket that screens for incoming targeted traffic with a precise Magic Byte sequence by hooking a BPF filter onto the uncooked socket.
“When BPFdoor finds a packet that contains its Magic Bytes in the filtered site visitors, it will treat it as a message from its operator and will parse out two fields and will all over again fork by itself,” the scientists explained.
“The guardian system will go on and check the filtered targeted visitors coming via the socket whilst the kid will treat the previously parsed fields as a command-and-management IP-Port blend and will endeavor to speak to it.”
Impending WEBINARLearn to Quit Ransomware with Serious-Time Security
Be a part of our webinar and discover how to stop ransomware attacks in their tracks with authentic-time MFA and assistance account protection.
Conserve My Seat!
In the closing stage, BPFDoor sets up an encrypted reverse shell session with the C2 server and awaits further more directions to be executed on the compromised machine.
The actuality that BPFDoor has remained concealed for a prolonged period speaks to its sophistication, what with risk actors significantly building malware targeting Linux methods owing to their prevalence in business and cloud environments.
The growth arrives as Google introduced a new extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) fuzzing framework referred to as Buzzer to aid harden the Linux kernel and make certain that sandboxed packages that operate in a privileged context are valid and protected.
The tech big more stated the tests process led to the discovery of a security flaw (CVE-2023-2163) that could be exploited to realize arbitrary reading and writing of kernel memory.
Uncovered this post intriguing? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through extra unique written content we submit.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Card ‘ID Theft’ Fraud Doubles in 2022
Card ‘ID Theft’ Fraud Doubles in 2022