Vulnerable Redis solutions have been targeted by a “new, improved, unsafe” variant of a malware termed SkidMap that’s engineered to goal a wide vary of Linux distributions.
“The malicious character of this malware is to adapt to the technique on which it is executed,” Trustwave security researcher Radoslaw Zdonczyk explained in an assessment published very last week.
Some of the Linux distribution SkidMap sets its eyes on include Alibaba, Anolis, openEuler, EulerOS, Stream, CentOS, RedHat, and Rocky.
SkidMap was initial disclosed by Trend Micro in September 2019 as a cryptocurrency mining botnet with capabilities to load malicious kernel modules that can obfuscate its functions as perfectly as check the miner method.

The operators of the malware have also been located camouflaging their backup command-and-handle (C2) IP address on the Bitcoin blockchain, evocative of yet another botnet malware acknowledged as Glupteba.
“The procedure of fetching true-time details from a decentralized and primarily uncensorable information resource to create a C2 IP tackle makes the infection hard to acquire down and helps make pivoting the C2 IP deal with simple and quick,” Akamai famous in February 2021.
The latest attack chain documented by Trustwave consists of breaching inadequately secured Redis server scenarios to deploy a dropper shell script that’s intended to distribute an ELF binary that masquerades as a GIF graphic file.
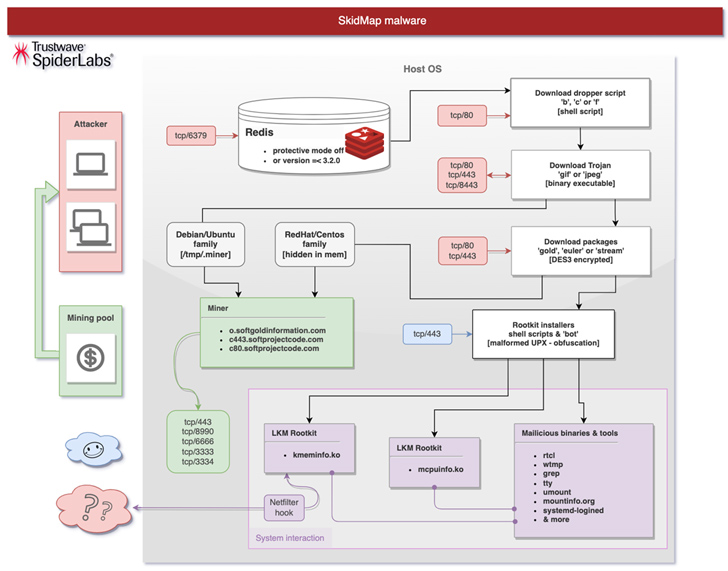
The binary then proceeds to include SSH keys to the “/root/.ssh/authoried_keys” file, disable SELinux, set up a reverse shell that pings an actor-managed server every single 60 minutes, and in the end obtain an correct bundle (named gold, stream, or euler) based on the Linux distribution and the kernel used.

The package deal, for its element, arrives with various shell scripts to set up the kernel modules and acquire methods to cover up the tracks by purging logs, and launch a botnet component capable of retrieving more rootkit payloads: mcpuinfo.ko, to conceal the miner method, and kmeminfo.ko, to assess, modify, or drop network packets.
Also downloaded is the miner binary itself, even though in some variants, a “built-in miner from an extracted ‘GIF’ binary file” is employed.
“The level of development of this malware is actually significant, and detecting it, especially in larger server infrastructures, can be really really hard,” Zdonczyk explained. “When tests it on house desktops, the only critical indicator that a little something was improper was the extreme procedure of admirers, and in the situation of laptops, the temperature of the circumstance.”
Discovered this article exciting? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to study extra special written content we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 FBI Alert: Crypto Scammers are Masquerading as NFT Developers
FBI Alert: Crypto Scammers are Masquerading as NFT Developers