A subtle Magecart marketing campaign has been observed manipulating websites’ default 404 mistake web site to conceal malicious code in what’s been described as the latest evolution of the assaults.
The action, for every Akamai, targets Magento and WooCommerce internet websites, with some of the victims belonging to big companies in the food stuff and retail industries.
“In this marketing campaign, all the target sites we detected have been directly exploited, as the malicious code snippet was injected into just one of their very first-social gathering methods,” Akamai security researcher Roman Lvovsky stated in a Monday investigation.
This includes inserting the code specifically into the HTML pages or within one of the to start with-occasion scripts that were being loaded as element of the web site.
The assaults are understood by means of a multi-stage chain, in which the loader code retrieves the principal payload for the duration of runtime in purchase to capture the delicate details entered by visitors on checkout webpages and exfiltrate it to a remote server.

“The reason of separating the attack into three sections is to conceal the attack in a way that would make it more complicated to detect,” Lvovsky discussed. “This will make the attack additional discreet and much more hard to detect by security providers and exterior scanning resources that could possibly be in put on the focused internet site.”
“This allows for the activation of the entire stream of the attack only on the especially qualified internet pages that is, mainly because of the obfuscation steps used by the attacker, the activation of the total attack movement can only manifest the place the attacker supposed for it to execute.”
The use of 404 mistake webpages is just one of the a few versions of the campaign, the other two of which obfuscate the skimmer code in a malformed HTML image tag’s onerror attribute and as an inline script that masquerades as the Meta Pixel code snippet.

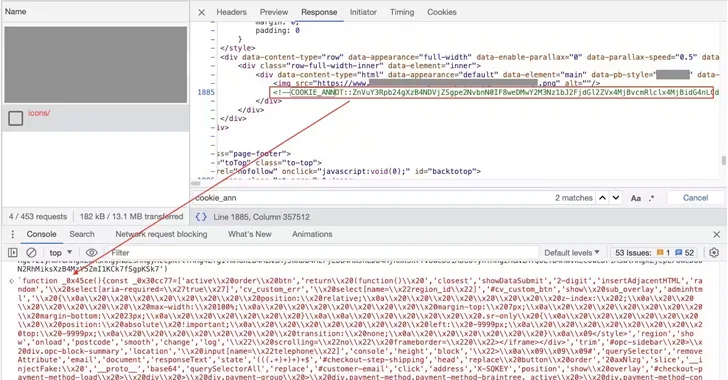
The pretend Meta Pixel code, for its part, fetches a PNG image from the website’s individual listing that has a Foundation64-encoded string appended to the end of the picture binary file, which, when decoded, represents a piece of JavaScript code that reaches out to an actor-controlled domain to retrieve the 2nd phase payload.
“This code is dependable for carrying out many malicious routines on the specific delicate website page, with the targets of looking through the user’s sensitive particular and credit score card details and transmitting it again to the skimmer’s C2 server,” Lvovsky reported.
Both equally these methods are intended to circumvent security measures these as static examination and external scanning, correctly prolonging the lifespan of the attack chain.

Even so, it is really the 3rd loader variant that stands out for its unusual concealment approach by using gain of default mistake web pages on the web-site. Appearing possibly as an inline script or a bogus Meta Pixel code, it sends a GET request to a non-existent URL in the web page, triggering a “404 Not Identified” reaction.
This response points to a modified error webpage hiding the skimmer code within it. The skimmer functions by overlaying a lookalike payment type on checkout pages to seize the data for subsequent exfiltration in the kind of a Foundation64-encoded string.
“The notion of manipulating the default 404 mistake web site of a targeted web page can offer you Magecart actors a variety of imaginative selections for enhanced hiding and evasion,” Lvovsky said.
“The ask for to the very first-party path foremost to the 404 web site is another evasion technique that can bypass Information Security Coverage headers and other security measures that may perhaps be actively analyzing network requests on the page.”
Located this short article fascinating? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to browse more exclusive material we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 libcue Library Flaw Opens GNOME Linux Systems Vulnerable to RCE Attacks
libcue Library Flaw Opens GNOME Linux Systems Vulnerable to RCE Attacks