Microsoft on Tuesday disclosed the intrusion activity aimed at Indian electrical power grid entities previously this year possible concerned the exploitation of security flaws in a now-discontinued web server called Boa.
The tech behemoth’s cybersecurity division stated the susceptible part poses a “offer chain risk that could have an impact on tens of millions of businesses and products.”
The conclusions construct on a prior report posted by Recorded Future in April 2022, which delved into a sustained marketing campaign orchestrated by suspected China-linked adversaries to strike critical infrastructure businesses in India.
The cybersecurity agency attributed the attacks to a previously undocumented danger cluster called Danger Exercise Team 38. When the Indian governing administration described the attack as unsuccessful “probing attempts,” China denied it was guiding the campaign.
The connections to China stem from the use of a modular backdoor dubbed ShadowPad, which is recognized to be shared amid numerous espionage teams that carry out intelligence-collecting missions on behalf of the country.
Though the precise first an infection vector made use of to breach the networks continues to be unfamiliar, the ShadowPad implant was managed by making use of a network of compromised internet-going through DVR/IP digicam equipment.
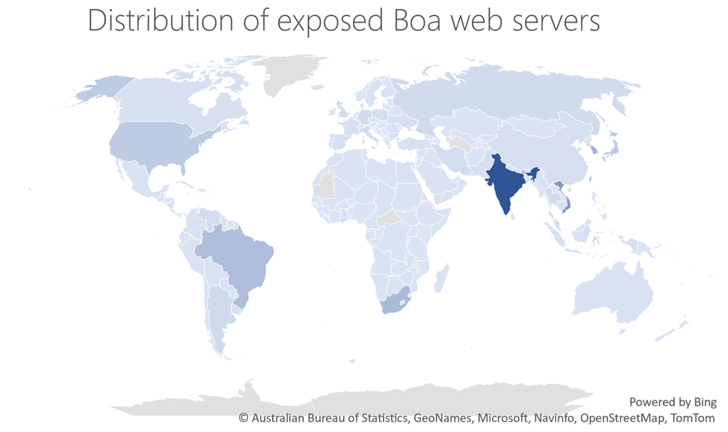
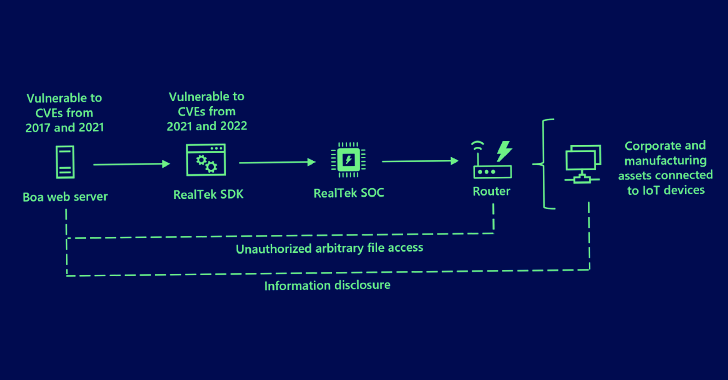
Microsoft reported its individual investigation into the attack activity uncovered Boa as a prevalent link, examining that the intrusions were directed versus exposed IoT units managing the web server.
“Inspite of becoming discontinued in 2005, the Boa web server continues to be executed by diverse distributors throughout a wide range of IoT devices and common software program progress kits (SDKs),” the firm reported.
“Devoid of developers handling the Boa web server, its recognised vulnerabilities could allow attackers to silently gain access to networks by collecting facts from documents.”
The most current conclusions once once more underscore the provide chain risk arising out of flaws in widely-utilized network parts, which could expose critical infrastructure to breaches through publicly-accessible products operating the susceptible web server.
Microsoft even further claimed it detected extra than just one million internet-uncovered Boa server elements worldwide in a single 7 days, with sizeable concentrations in India.
The pervasive character of Boa servers is attributed to the reality that they are integrated into greatly-employed SDKs, this sort of as those from RealTek, which are then bundled with units like routers, access factors, and repeaters.
The intricate character of the software package source chain indicates that fixes from an upstream vendor may not trickle down to consumers and that unresolved flaws could go on to persist irrespective of firmware updates from downstream companies.
Some of the large-severity bugs influencing Boa include things like CVE-2017-9833 and CVE-2021-33558, which, if correctly exploited, could permit malicious hacking groups to go through arbitrary documents, acquire delicate information, and realize remote code execution.
Weaponizing these unpatched shortcomings could additional help menace actors to glean a lot more details about the specific IT environments, effectively making way for disruptive assaults.
“The acceptance of the Boa web server displays the prospective exposure risk of an insecure supply chain, even when security greatest techniques are utilized to equipment in the network,” Microsoft said.
“As attackers seek new footholds into ever more secure gadgets and networks, identifying and blocking distributed security challenges by program and components supply chains, like out-of-date factors, must be prioritized by organizations.”
Observed this posting exciting? Observe THN on Fb, Twitter and LinkedIn to read through additional exceptional information we put up.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Meta Quest 2 bundle with 'Resident Evil 4' and 'Beat Saber' is just $350 for Black Friday
Meta Quest 2 bundle with 'Resident Evil 4' and 'Beat Saber' is just $350 for Black Friday