Cybersecurity researchers have found out a new campaign that is exploiting a recently disclosed security flaw in Fortinet FortiClient EMS devices to provide ScreenConnect and Metasploit Powerfun payloads.
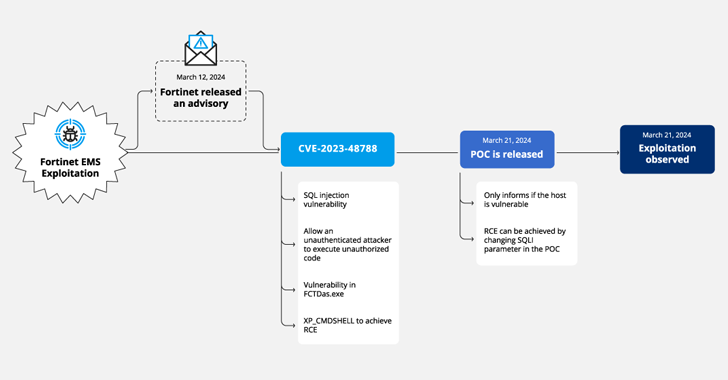
The activity entails the exploitation of CVE-2023-48788 (CVSS score: 9.3), a critical SQL injection flaw that could allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute unauthorized code or instructions by way of specially crafted requests.
Cybersecurity organization Forescout is monitoring the marketing campaign beneath the codename Connect:enjoyable owing to the use of ScreenConnect and Powerfun for put up-exploitation.

The intrusion focused an unnamed media enterprise that had its vulnerable FortiClient EMS product uncovered to the internet soon right after the launch of a proof-of-idea (PoC) exploit for the flaw on March 21, 2024.
In excess of the subsequent few of days, the unfamiliar adversary was noticed leveraging the flaw to unsuccessfully obtain ScreenConnect and then put in the distant desktop program utilizing the msiexec utility.
Nevertheless, on March 25, the PoC exploit was utilised to launch PowerShell code that downloaded Metasploit’s Powerfun script and initiated a reverse link to a further IP address.
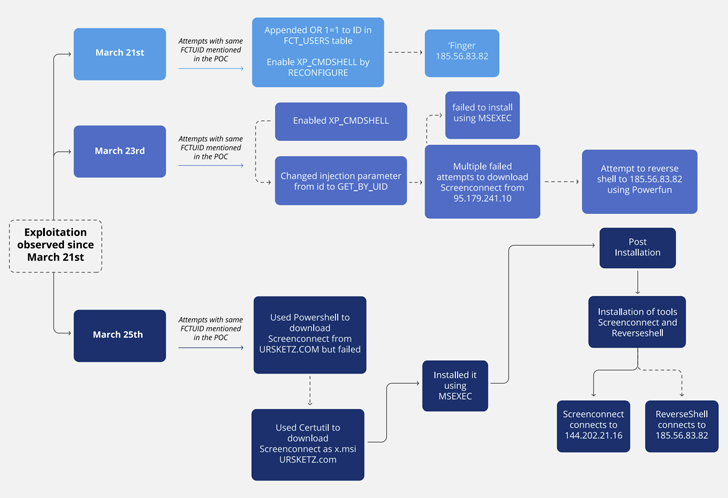
Also detected had been SQL statements designed to obtain ScreenConnect from a remote domain (“ursketz[.]com”) using certutil, which was then put in by using msiexec in advance of developing connections with a command-and-handle (C2) server.
There is proof to counsel that the menace actor driving it has been lively due to the fact at the very least 2022, particularly singling out Fortinet appliances and using Vietnamese and German languages in their infrastructure.
“The observed exercise plainly has a handbook part evidenced by all the failed tries to down load and install equipment, as well as the reasonably prolonged time taken involving tries,” security researcher Sai Molige reported.

“This is proof that this action is component of a specific campaign, somewhat than an exploit provided in automated cybercriminal botnets. From our observations, it seems that the actors guiding this campaign are not mass scanning but picking focus on environments that have VPN appliances.”
Forescout mentioned the attack shares tactical and infrastructure overlaps with other incidents documented by Palo Alto Networks Device 42 and Blumira in March 2024 that contain the abuse of CVE-2023-48788 to down load ScreenConnect and Atera.
Businesses are recommended to use patches offered by Fortinet to tackle potential threats, observe for suspicious targeted visitors, and use a web software firewall (WAF) to block possibly destructive requests.
Identified this short article attention-grabbing? Stick to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through more special content material we publish.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Cisco Warns of Global Surge in Brute-Force Attacks Targeting VPN and SSH Services
Cisco Warns of Global Surge in Brute-Force Attacks Targeting VPN and SSH Services