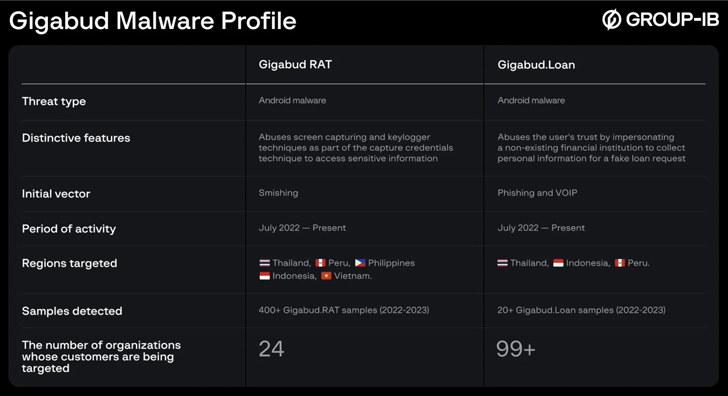
Account holders of in excess of various money institutions in Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Peru are staying focused by an Android banking malware called Gigabud RAT.
“Just one of Gigabud RAT’s exclusive capabilities is that it will not execute any malicious actions until the person is authorized into the destructive software by a fraudster, […] which makes it more difficult to detect,” Group-IB scientists Pavel Naumov and Artem Grischenko mentioned.
“As an alternative of employing HTML overlay assaults, Gigabud RAT gathers delicate details primarily through display recording.”
Gigabud RAT was 1st documented by Cyble in January 2023 right after it was spotted impersonating lender and government apps to siphon delicate details. It can be acknowledged to be energetic in the wild because at least July 2022.
The Singapore-dependent company reported it also determined a next variant of the malware minus the RAT abilities. Dubbed Gigabud.Bank loan, it arrives below the guise of a financial loan software that is able of exfiltrating user-input information.
“The targets ended up individuals lured into filling out a lender card software form to receive a low-desire financial loan,” the scientists said. “The victims are persuaded to give individual data for the duration of the application procedure.”
Both equally malware variations are unfold via phishing websites, the backlinks to which are shipped to victims by way of SMS or quick messages on social media networks. Gigabud.Personal loan is also distributed right in the variety of APK data files despatched by messages on WhatsApp.

Targets who are approached on social media are normally coerced into going to the web sites below the pretext of finishing a tax audit and boasting a refund.
Whilst Android devices have the “Install from Unidentified Sources” placing disabled by default as a security measure to avoid the installation of apps from untrusted sources, the working method makes it possible for other applications on mounted on the system, these kinds of as web browsers, email purchasers, file managers, and messaging apps, to request the “Request_Put in_Offers” authorization.
Ought to a consumer grant permission to these types of apps, it enables the danger actors to put in rogue APK data files when bypassing the “Put in from Unknown Sources” option.
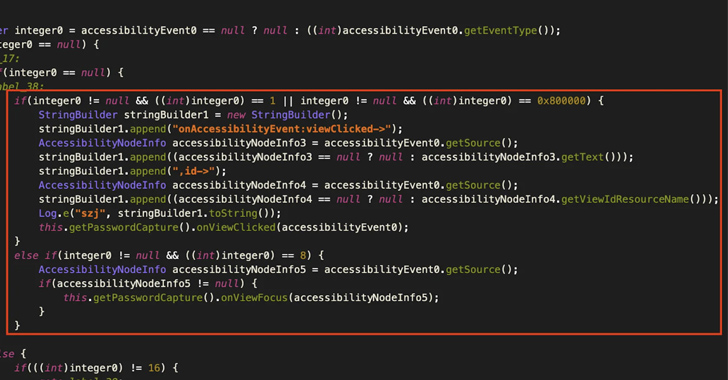
Gigabud capabilities a good deal like other Android banking trojans by requesting for accessibility services permissions to conduct monitor capturing and logging keystrokes. It’s also geared up to swap bank card numbers in clipboards and accomplish automatic fund transfers as a result of distant entry.
On the other hand, Gigabud.Personal loan features as a tool to gather particular information and facts this kind of as full name, id amount, countrywide identity doc picture, digital signature, education, profits info, lender card details, and phone selection underneath the guise of distributing a loan ask for to the financial institution.
The findings abide by the discovery of 43 rogue applications on the Google Perform Keep that load adverts whilst the device’s display is turned off. The applications, with cumulative downloads of 2.5 million, have considering the fact that been taken down or up to date by the builders to remove the advert fraud ingredient.
McAfee stated the adware, when mounted, seeks users’ permissions to exclude the apps when saving battery and let it to attract more than other apps, successfully opening the door to additional malevolent assaults, this sort of as loading ads in the history and exhibiting phishing webpages.
The advertisement fraud library utilized by the apps also employs hold off tactics to evade detection and can be remotely modified by the operators utilizing the Firebase messaging services, lending it an supplemental layer of complexity.
The disclosure arrives as the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is warning of an boost in scammers pretending to be restoration and tracing companies that can help victims of cryptocurrency financial commitment ripoffs get back dropped property.
“Recovery scheme fraudsters charge an up-entrance price and both stop conversation with the target just after obtaining an first deposit or make an incomplete or inaccurate tracing report and request added service fees to get well money,” the FBI stated.

On best of that, the company has cautioned that cybercriminals are embedding nefarious code in cell beta-tests apps masquerading as legitimate cryptocurrency expense apps to defraud likely victims by facilitating the theft of personally identifiable information (PII) and economic account facts.
“The apps may possibly seem legit by applying names, photographs, or descriptions comparable to popular applications,” the company spelled out. “Cyber criminals generally use phishing or romance scams to create communications with the sufferer, then direct the target to obtain a mobile beta-tests application housed inside of a mobile beta-tests app surroundings, promising incentives this sort of as massive financial payouts.”
In these schemes, danger actors get in touch with probable victims on dating and social networking apps and create trust with the supreme intention to entice them into downloading pre-release variations of the applications.
“The victims enter authentic account information into the application, sending income they believe will be invested in cryptocurrency, but rather the victim resources are despatched to the cyber criminals,” the FBI mentioned.
It truly is worth noting that the abuse of Apple’s TestFlight beta testing framework to carry out pig butchering frauds was highlighted by cybersecurity agency Sophos last calendar year.
The latest waves of the campaign, also referred to as CryptoRom, have weaponized Apple’s company and developer ad-hoc app distribution strategies to deliver bogus crypto apps in a bid to slip past constraints that avert end users from downloading iOS apps outside of the Application Keep.
In other occasions, a seemingly innocuous application is trojanized just after it is authorised and published to the Apple and Google application storefronts by altering the distant code to stage to an attacker-managed server to introduce destructive actions.
Identified this write-up intriguing? Stick to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read extra unique information we publish.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Over 120,000 Computers Compromised by Info Stealers Linked to Users of Cybercrime Forums
Over 120,000 Computers Compromised by Info Stealers Linked to Users of Cybercrime Forums