Cybersecurity scientists have disclosed aspects of a now-patched zero-day flaw in Google Cloud System (GCP) that could have enabled danger actors to conceal an unremovable, malicious application inside a victim’s Google account.
Dubbed GhostToken by Israeli cybersecurity startup Astrix Security, the shortcoming impacts all Google accounts, including enterprise-targeted Workspace accounts. It was uncovered and described to Google on June 19, 2022. The corporation deployed a international-patch additional than nine months afterwards on April 7, 2023.
“The vulnerability […] allows attackers to attain everlasting and unremovable access to a victim’s Google account by changing an previously authorized 3rd-get together application into a malicious trojan app, leaving the victim’s individual details uncovered permanently,” Astrix said in a report.
In a nutshell, the flaw makes it probable for an attacker to disguise their malicious app from a victim’s Google account software administration page, therefore properly avoiding end users from revoking its accessibility.
This is accomplished by deleting the GCP job involved with the licensed OAuth software, resulting in it to go in a “pending deletion” point out. The threat actor, armed with this ability, could then unhide the rogue application by restoring the task and use the obtain token to obtain the victim’s data, and make it invisible yet again.
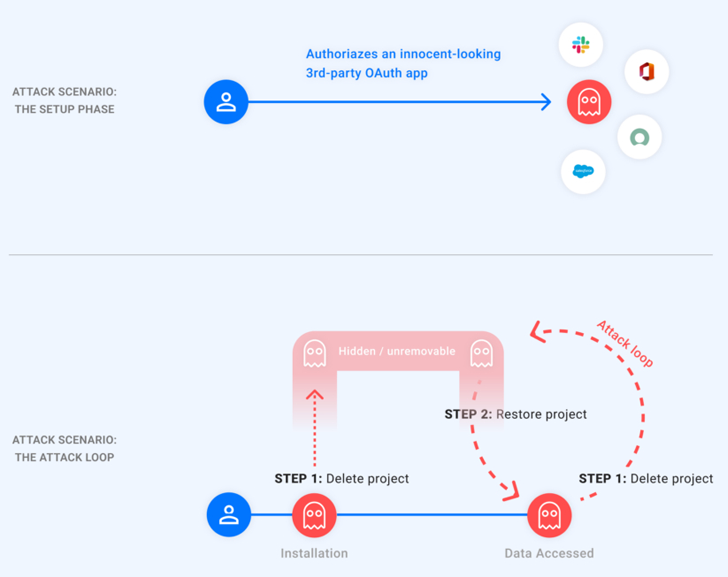
“In other words and phrases, the attacker holds a ‘ghost’ token to the victim’s account,” Astrix reported.
The form of data that can be accessed relies upon on the permissions granted to the application, which the adversaries can abuse to delete files from Google Generate, compose email messages on the victim’s behalf to conduct social engineering attacks, keep track of areas, and exfiltrate delicate facts from Google Calendar, Images, and Drive.
“Victims may perhaps unknowingly authorize entry to these kinds of malicious applications by putting in a seemingly harmless app from the Google Market or just one of the numerous efficiency applications out there on the web,” Astrix extra.
Future WEBINARZero Rely on + Deception: Discover How to Outsmart Attackers!
Explore how Deception can detect superior threats, prevent lateral movement, and greatly enhance your Zero Belief method. Be a part of our insightful webinar!
Preserve My Seat!
“After the malicious app has been licensed, an attacker exploiting the vulnerability can bypass Google’s “Applications with entry to your account” administration attribute, which is the only spot where by Google customers can view third-get together applications related to their account.”
Google’s patch addresses the trouble by now displaying apps that are in a pending deletion condition on the third-party entry webpage, permitting end users to revoke the authorization granted to this sort of applications.
The enhancement comes as Google Cloud fastened a privilege escalation flaw in the Cloud Asset Inventory API dubbed Asset Key Thief that could be exploited to steal person-managed Support Account private keys and gain obtain to useful knowledge. The issue, which was learned by SADA previously this February, was patched by the tech large on March 14, 2023.
The results occur a little over a thirty day period right after cloud incident response firm Mitiga revealed that adversaries could choose advantage of “insufficient” forensic visibility into GCP to exfiltrate delicate facts.
Observed this post interesting? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through more exclusive content material we submit.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 14 Kubernetes and Cloud Security Challenges and How to Solve Them
14 Kubernetes and Cloud Security Challenges and How to Solve Them