German and South Korean authorities organizations have warned about cyber attacks mounted by a threat actor tracked as Kimsuky applying rogue browser extensions to steal users’ Gmail inboxes.
The joint advisory arrives from Germany’s domestic intelligence equipment, the Federal Business office for the Security of the Constitution (BfV), and South Korea’s Countrywide Intelligence Support of the Republic of Korea (NIS).
The intrusions are made to strike “professionals on the Korean Peninsula and North Korea issues” by way of spear-phishing campaigns, the businesses mentioned.
Kimsuky, also recognized Black Banshee, Thallium, and Velvet Chollima, refers to a subordinate component in just North Korea’s Reconnaissance Typical Bureau and is known to “obtain strategic intelligence on geopolitical occasions and negotiations influencing the DPRK’s passions.”
Principal targets of curiosity incorporate entities in the U.S. and South Korea, specially singling out people working inside of the federal government, military services, manufacturing, academic, and feel tank businesses.
“This danger actor’s actions include collecting money, private, and consumer facts specifically from tutorial, producing, and countrywide security industries in South Korea,” Google-owned risk intelligence company Mandiant disclosed past 12 months.
New assaults orchestrated by the team propose an expansion of its cyber exercise to encompass Android malware strains these kinds of as FastFire, FastSpy, FastViewer, and RambleOn.
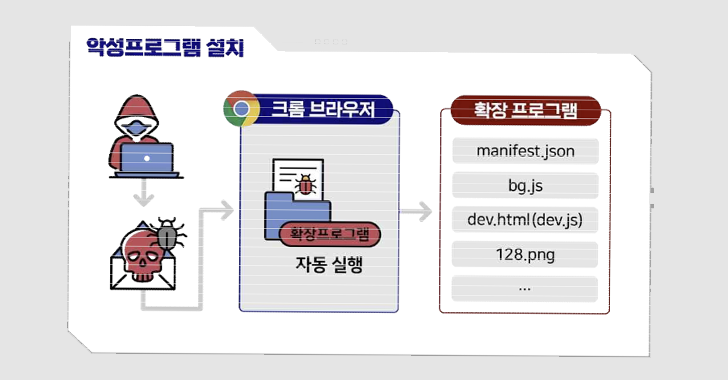
The use of Chromium-dependent browser extensions for cyber espionage needs is not new for Kimsuky, which has previously used similar procedures as element of campaigns tracked as Stolen Pencil and SharpTongue.
The SharpTongue operation also overlaps with the most recent work in that the latter is also capable of stealing a victim’s email content material utilizing the rogue add-on, which, in switch, leverages the browser’s DevTools API to accomplish the purpose.
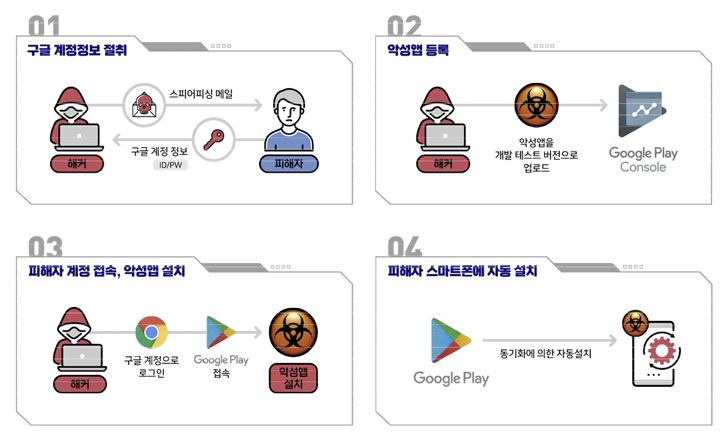
But in an escalation of Kimsuky’s mobile attacks, the risk actor has been noticed logging into victims’ Google accounts working with credentials already received in progress through phishing practices and then setting up a destructive application on the gadgets connected to the accounts.
“The attacker logs in with the victim’s Google account on the Computer system, accesses the Google Play Shop, and requests the installation of a destructive application,” the organizations discussed. “At this time, the target’s smartphone joined with the Google account is selected as the product to put in the destructive app on.”
It is suspected that the apps, which embed FastFire and FastViewer, are distributed working with a Google Engage in feature known as “internal screening” that allows 3rd-celebration builders to distribute their apps to a “tiny established of trusted testers.”
WEBINARDiscover the Hidden Potential risks of 3rd-Social gathering SaaS Apps
Are you knowledgeable of the pitfalls involved with third-social gathering app obtain to your firm’s SaaS apps? Join our webinar to discover about the forms of permissions currently being granted and how to lower risk.
RESERVE YOUR SEAT
A position worthy of mentioning below is that these inside app assessments, which are carried out prior to releasing the app to production, simply cannot exceed 100 customers for every app, indicating that the campaign is very targeted in character.
Both the malware-laced apps occur with capabilities to harvest a vast vary of sensitive data by abusing Android’s accessibility providers. The apps are mentioned down below –
- com.viewer.fastsecure (FastFire)
- com.tf.thinkdroid.secviewer (FastViewer)
The disclosure comes as the North Korean advanced persistent risk (APT) actor dubbed ScarCruft has been joined to various attack vectors that are used to produce PowerShell-centered backdoors onto compromised hosts.
Observed this posting interesting? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through much more exclusive information we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 New Android Banking Trojan ‘Nexus’ Promoted As MaaS
New Android Banking Trojan ‘Nexus’ Promoted As MaaS