At minimum 50 % of dozen GitHub accounts from phony scientists involved with a fraudulent cybersecurity corporation have been observed pushing malicious repositories on the code hosting provider.
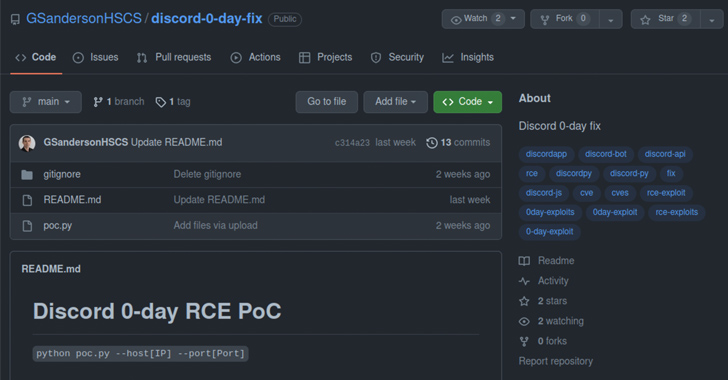
All seven repositories, which are however out there as of crafting, assert to be a proof-of-idea (PoC) exploit for purported zero-day flaws in Discord, Google Chrome, and Microsoft Exchange.
VulnCheck, which identified the action, said, “the people today generating these repositories have put considerable energy into generating them appear legit by building a network of accounts and Twitter profiles, pretending to be section of a non-existent company named Superior Sierra Cyber Security.”

The cybersecurity company claimed it initially arrived throughout the rogue repositories in early May perhaps when they were being observed pushing comparable PoC exploits for zero-day bugs in Signal and WhatsApp. The two repositories have due to the fact been taken down.
Besides sharing some of the purported results on Twitter in an try to build legitimacy, the network of accounts even takes advantage of headshots of precise security scientists from firms like Immediate7, suggesting that the danger actors place important effort and hard work into crafting the campaign.
The PoC is a Python script that is designed to obtain a malicious binary and execute it on the victim’s functioning method, be it Windows or Linux.
Upcoming WEBINAR🔐 Mastering API Security: Comprehension Your Real Attack Floor
Discover the untapped vulnerabilities in your API ecosystem and consider proactive steps in the direction of ironclad security. Be a part of our insightful webinar!
Join the Session.wn-button,.wn-label,.wn-label:right afterdisplay screen:inline-block.test_two_webinarmargin:20px 10px 30px 0background:#f9fbffcolor:#160755padding: 5%border:2px solid #d9deffborder-radius:10pxtext-align:leftbox-shadow:10px 10px #e2ebff-webkit-border-leading-still left-radius:25px-moz-border-radius-topleft:25px-webkit-border-base-proper-radius:25px-moz-border-radius-bottomright:25px.wn-labelfont-dimensions:13pxmargin:20px 0font-body weight:600letter-spacing:.6pxcolor:#596cec.wn-label:afterwidth:50pxheight:6pxcontent:”border-leading:2px stable #d9deffmargin: 8px.wn-titlefont-dimensions:21pxpadding:10px 0font-fat:900textual content-align:leftline-height:33px.wn-descriptiontextual content-align:leftfont-size:15.6pxline-top:26pxmargin:5px !importantcolor:#4e6a8d.wn-buttonpadding:6px 12pxborder-radius:5pxbackground-shade:#4469f5font-size:15pxcolor:#fff!importantborder:0line-top:inherittext-decoration:none!importantcursor:pointermargin:15px 20pxfloat:leftfont-bodyweight:500letter-spacing:.2px
“The attacker has built a whole lot of energy to produce all these faux personas, only to deliver very evident malware,” VulnCheck researcher Jacob Baines mentioned. “It is really unclear if they have been successful, but supplied that they have ongoing to go after this avenue of attacks, it appears to be they believe that they will be effective.”
It can be at present not known if this is the function of an amateur actor or an innovative persistent threat (APT). But security scientists have beforehand appear beneath the radar of North Korean country-point out teams, as revealed by Google in January 2021.
If just about anything, the findings display the need to have for training caution when it arrives to downloading code from open supply repositories. It is also essential that people scrutinize the code prior to execution to make sure they never pose any security hazards.
Located this write-up fascinating? Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to study far more unique articles we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 MFA Bypass Kits Account For One Million Monthly Messages
MFA Bypass Kits Account For One Million Monthly Messages