An investigation into info safety labels for Android applications available on the Google Participate in Retail store has uncovered “severe loopholes” that enable apps to offer misleading or outright bogus information and facts.
The examine, executed by the Mozilla Foundation as section of its *Privacy Not Integrated initiative, compared the privateness guidelines and labels of the 20 most popular paid out apps and the 20 most popular free applications on the app market.
It uncovered that, in around 80% of the apps reviewed, “the labels had been false or misleading dependent on discrepancies between the apps’ privacy insurance policies and the information and facts apps self-reported on Google’s Knowledge protection kind.”
“The apps are not self-reporting accurately adequate to give the public any meaningful reassurance about the safety and privacy of their knowledge,” Mozilla further more explained, introducing individuals are being led to “consider these apps are executing a improved career defending their privacy than they are.”
Three of the applications – UC Browser – Risk-free, Quick, Personal League of Stickman Acti and Terraria – did not have their Data security sections crammed at all. A mere 6 of the 40 apps acquired an “Ok” quality.
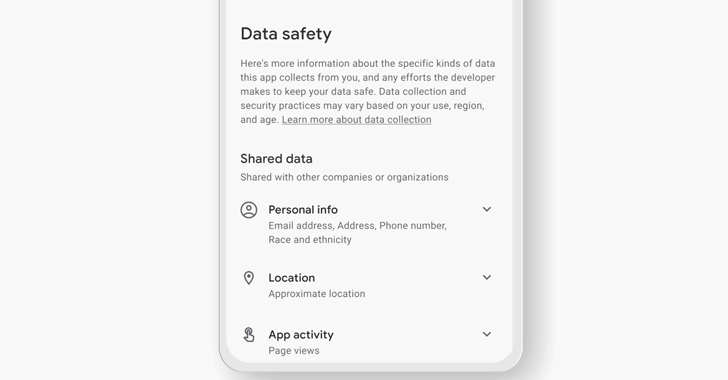
Final yr, Google started rolling out a new Knowledge protection segment on the Participate in Retailer that spells out the apps’ privacy and security tactics. It can be also the company’s answer to Apple’s application privacy labels that came into result in December 2020.
Nevertheless, there are some very important variances. Apple’s labels emphasize on what information is remaining gathered, together with these that are gathered for tracking applications as perfectly as facts that’s joined to the consumers.
Google’s labels, on the other hand, will allow builders to deliver additional context as to why these kinds of a details selection may well be necessary and the security principles that are utilized to safeguard the info.
That stated, each methods depend on developers to be clear about how their apps use information. Although Apple has instituted schedule checks to guarantee that the labels do not give a phony feeling of security, Google leaves developers to make “finish and precise declarations.”
Now in accordance to Mozilla, these self-claimed labels could not be an accurate illustration of an app’s knowledge-gathering insurance policies, calling into dilemma the efficiency of these kinds of a framework in enhancing privacy transparency and enabling users to make educated selections.
“For example, Google exempts apps sharing data with ‘service providers’ from its disclosure necessities, which is problematic because of to equally the narrow definition it utilizes for services vendors and the substantial sum of shopper facts concerned,” Mozilla claimed.
To that finish, Mozilla refutes Snapchat, TikTok and Twitter’s promises that their applications do not “share consumer details with other corporations or companies,” stating that the apps’ privateness insurance policies explicitly point out sharing person details with advertisers and internet service providers, among some others.
It really is truly worth pointing out right here that applications can be exempted from disclosing info sharing presented they have sought users’ consent, if the knowledge is getting shared with a developer’s services provider, or if the information is totally anonymized.
The American non-revenue is also recommending Apple and Google to adopt a common nutrition labeling common, along with urging the tech giants to “clarify their enforcement motion in opposition to apps that never comply and acquire some duty for making certain the precision of the information and facts apps report.”
Identified this write-up interesting? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through a lot more special information we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Solving a machine-learning mystery
Solving a machine-learning mystery