A suspected Chinese-nexus hacking team exploited a recently disclosed zero-working day flaw in Barracuda Networks Email Security Gateway (ESG) appliances to breach governing administration, army, protection and aerospace, significant-tech marketplace, and telecom sectors as section of a world wide espionage campaign.
Mandiant, which is monitoring the action under the name UNC4841, explained the menace actor as “very responsive to defensive attempts” and capable of actively tweaking their modus operandi to preserve persistent access to targets.
“UNC4841 deployed new and novel malware intended to manage existence at a small subset of superior priority targets that it compromised both before the patch was introduced, or shortly subsequent Barracuda’s remediation advice,” the Google-owned risk intelligence agency stated in a new specialized report posted currently.
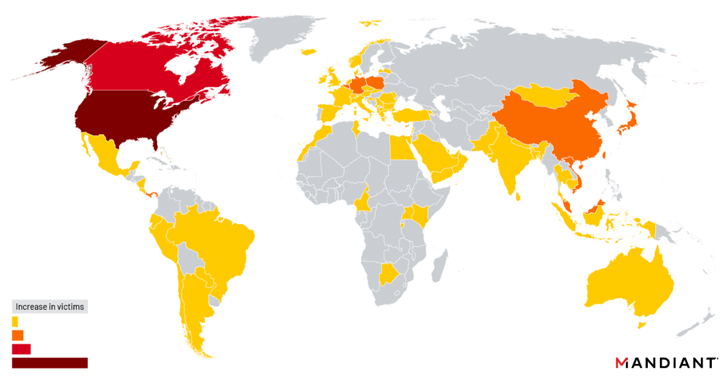
Practically a 3rd of the recognized affected corporations are authorities businesses. Interestingly sufficient, some of the earliest compromises look to have taken location on a compact number of products geolocated to mainland China.
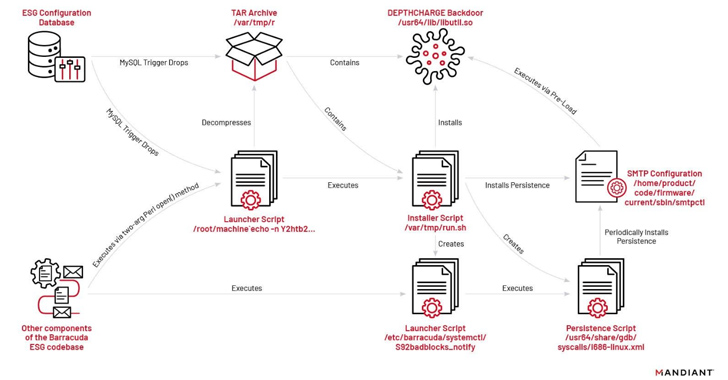
The attacks entail the exploitation of CVE-2023-2868 to deploy malware and conduct write-up-exploitation pursuits. In pick out cases, the intrusions have led to the deployment of supplemental malware, such as SUBMARINE (aka DEPTHCHARGE), to maintain persistence in response to remediation endeavors.
Additional analysis of the marketing campaign has disclosed a “distinctive tumble off in exercise from around January 20 to January 22, 2023,” coinciding with the commencing of the Chinese New 12 months, followed by two surges, just one following Barracuda’s general public notification on May possibly 23, 2023, and a next just one in early June 2023.

The latter is said to have concerned the attacker “making an attempt to maintain accessibility to compromised environments via the deployment of the new malware people SKIPJACK, DEPTHCHARGE, and FOXTROT / FOXGLOVE.”
When SKIPJACK is a passive implant that registers a listener for specific incoming email headers prior to decoding and working their written content, DEPTHCHARGE is pre-loaded into the Barracuda SMTP (BSMTP) daemon applying the LD_PRELOAD atmosphere variable, and retrieves encrypted commands for execution.
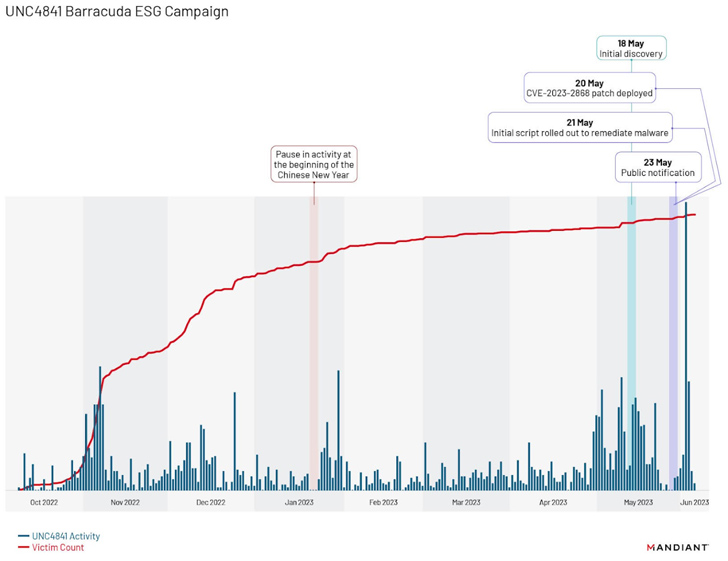
The earliest use of DEPTHCHARGE dates again to May 30, 2023, just days after Barracuda publicly disclosed the flaw. Mandiant stated it observed the malware remaining fast deployed to a subset of targets, indicating a superior stage of preparing and an attempt to persist in just high-value environments.
“It also suggests that inspite of this operation’s world wide protection, it was not opportunistic, and that UNC4841 had sufficient planning and funding to foresee and prepare for contingencies that could potentially disrupt their accessibility to concentrate on networks,” the enterprise spelled out.
Roughly 2.64 percent of the whole compromised appliances are approximated to have been contaminated with DEPTHCHARGE. This victimology spans U.S. and international government entities, as very well as superior-tech and details technology companies.
The 3rd malware strain, also selectively sent to targets, is FOXTROT, a C++ implant that is launched making use of a C-centered software dubbed FOXGLOVE. Communicating via TCP, it will come with characteristics to seize keystrokes, run shell commands, transfer information, and set up a reverse shell.
What’s far more, FOXTROT shares overlaps with an open-supply rootkit known as Reptile, which has been thoroughly applied by numerous Chinese hacking crews in recent months. This also comprises UNC3886, a menace actor connected to the zero-day exploitation of a now-patched medium-severity security flaw in the Fortinet FortiOS working system.
“FOXTROT and FOXGLOVE are also notable in that they are the only malware people observed currently being made use of by UNC4841 that were being not precisely intended for Barracuda ESGs,” Mandiant pointed out. “Centered on features, FOXTROT was probable also meant to be deployed to other Linux-dependent gadgets inside of a network to allow lateral movement and credential theft.”
An additional part that will make FOXGLOVE and FOXTROT stand out is the actuality that they have been the most selectively deployed amid all malware households utilised by UNC4841, completely using it to goal government or govt-related businesses.
The adversarial collective has also been detected undertaking inner reconnaissance and subsequent lateral movement steps inside a restricted number of sufferer environments. Far more than just one scenario entailed utilizing Microsoft Outlook Web Access (OWA) to endeavor to log in to mailboxes for customers in just the corporations.

As an alternative variety of remote accessibility, the highly developed persistent threat (APT) actor made accounts containing 4 randomly produced figures in the and many others/passwd file on about 5 % of the formerly impacted appliances.
UNC4841’s Chinese connections are more bolstered by the infrastructure commonalities involving the team and another uncategorized cluster codenamed UNC2286, which, in flip, shares overlaps with other Chinese espionage strategies tracked as FamousSparrow and GhostEmperor.
The most up-to-date disclosure arrives versus the backdrop of the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) urging impacted prospects to replace their ESG appliances with speedy outcome, citing continued risk.
“UNC4841 is a nicely-resourced actor that has used a vast variety of malware and intent-developed tooling to permit their world wide espionage operations,” the firm said, contacting out the risk actor’s capability to selectively deploy extra payloads to specific sufferer environments.
“Shared infrastructure and techniques for anonymization are prevalent amongst Chinese cyber espionage actors, as is shared tooling and very likely malware enhancement assets. It is very likely that we will keep on to notice Chinese cyber espionage operations targeting edge infrastructure with zero-day vulnerabilities and the deployment of malware custom made to certain appliance ecosystems.”
Identified this short article attention-grabbing? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through more distinctive content we post.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 DarkGate Malware Activity Spikes as Developer Rents Out Malware to Affiliates
DarkGate Malware Activity Spikes as Developer Rents Out Malware to Affiliates