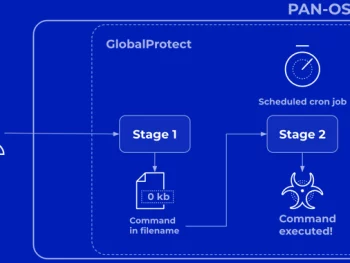
Palo Alto Networks Discloses More Details on Critical PAN-OS Flaw Under Attack
Palo Alto Networks has shared much more details of a critical security flaw impacting PAN-OS that has occur under lively exploitation in the wild by malicious actors. The corporation described the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-3400 (CVSS…
Palo Alto Networks Discloses More Details on Critical PAN-OS Flaw Under AttackRead More

Critical Update: CrushFTP Zero-Day Flaw Exploited in Targeted Attacks
People of the CrushFTP business file transfer software program are getting urged to update to the most recent version adhering to the discovery of a security flaw that has arrive below focused exploitation in the wild.…
Critical Update: CrushFTP Zero-Day Flaw Exploited in Targeted AttacksRead More
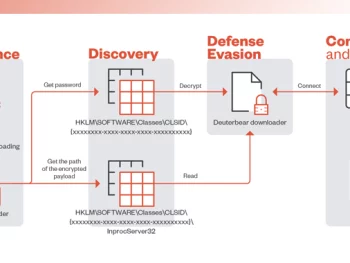
BlackTech Targets Tech, Research, and Gov Sectors New ‘Deuterbear’ Tool
Technology, investigate, and federal government sectors in the Asia-Pacific area have been focused by a risk actor called BlackTech as component of a new cyber attack wave. The intrusions pave the way for an updated variation…
BlackTech Targets Tech, Research, and Gov Sectors New ‘Deuterbear’ ToolRead More
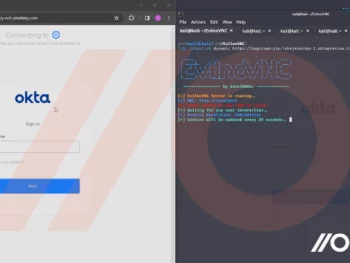
How Attackers Can Own a Business Without Touching the Endpoint
Attackers are increasingly building use of “networkless” attack procedures focusing on cloud applications and identities. Here’s how attackers can (and are) compromising businesses – with no at any time needing to contact the endpoint or conventional…
How Attackers Can Own a Business Without Touching the EndpointRead More

Akira Ransomware Gang Extorts $42 Million; Now Targets Linux Servers
Threat actors driving the Akira ransomware team have extorted roughly $42 million in illicit proceeds immediately after breaching the networks of extra than 250 victims as of January 1, 2024. “Since March 2023, Akira ransomware has…
Akira Ransomware Gang Extorts $42 Million; Now Targets Linux ServersRead More

Hackers Target Middle East Governments with Evasive “CR4T” Backdoor
Federal government entities in the Middle East have been qualified as component of a beforehand undocumented marketing campaign to deliver a new backdoor dubbed CR4T. Russian cybersecurity firm Kaspersky mentioned it uncovered the exercise in February…
Hackers Target Middle East Governments with Evasive “CR4T” BackdoorRead More









